Pathway activation profiling reveals new insights into age-related macular degeneration and provides avenues for therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 25543336
- PMCID: PMC4298366
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100711
Pathway activation profiling reveals new insights into age-related macular degeneration and provides avenues for therapeutic interventions
Abstract
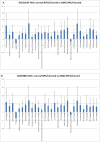
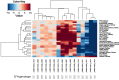
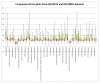
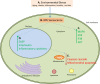
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a major cause of blindness in older people and is caused by loss of the central region of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). Conventional methods of gene expression analysis have yielded important insights into AMD pathogenesis, but the precise molecular pathway alterations are still poorly understood. Therefore we developed a new software program, "AMD Medicine", and discovered differential pathway activation profiles in samples of human RPE/choroid from AMD patients and controls. We identified 29 pathways in RPE-choroid AMD phenotypes: 27 pathways were activated in AMD compared to controls, and 2 pathways were activated in controls compared to AMD. In AMD, we identified a graded activation of pathways related to wound response, complement cascade, and cell survival. Also, there was downregulation of two pathways responsible for apoptosis. Furthermore, significant activation of pro-mitotic pathways is consistent with dedifferentiation and cell proliferation events, which occur early in the pathogenesis of AMD. Significantly, we discovered new global pathway activation signatures of AMD involved in the cell-based inflammatory response: IL-2, STAT3, and ERK. The ultimate aim of our research is to achieve a better understanding of signaling pathways involved in AMD pathology, which will eventually lead to better treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bourne RR, Stevens GA, White RA, Smith JL, Flaxman SR, Price H, Jonas JB, Keeffe J, Leasher J, Naidoo K, Pesudovs K, Resnikoff S, Taylor HR. Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis. The Lancet Global health. 2013;1:e339–349. - PubMed
-
- Wong WL, Su X, Li X, Cheung CM, Klein R, Cheng CY, Wong TY. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Global health. 2014;2:e106–116. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

