Intravital imaging reveals p53-dependent cancer cell death induced by phototherapy via calcium signaling
- PMID: 25544762
- PMCID: PMC4359305
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2935
Intravital imaging reveals p53-dependent cancer cell death induced by phototherapy via calcium signaling
Abstract
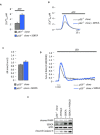
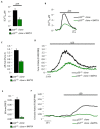
One challenge in biology is signal transduction monitoring in a physiological context. Intravital imaging techniques are revolutionizing our understanding of tumor and host cell behaviors in the tumor environment. However, these deep tissue imaging techniques have not yet been adopted to investigate the second messenger calcium (Ca²⁺). In the present study, we established conditions that allow the in vivo detection of Ca²⁺ signaling in three-dimensional tumor masses in mouse models. By combining intravital imaging and a skinfold chamber technique, we determined the ability of photodynamic cancer therapy to induce an increase in intracellular Ca²⁺ concentrations and, consequently, an increase in cell death in a p53-dependent pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures





Comment in
-
Inside the tumor: p53 modulates calcium homeostasis.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(7):933-4. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1010973. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25715001 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P. Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. NatRevMolCell Biol. 2003;4(7):552–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

