Impact of peripheral nerve block with low dose local anesthetics on analgesia and functional outcomes following total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study
- PMID: 25545781
- PMCID: PMC4674268
- DOI: 10.1111/pme.12652
Impact of peripheral nerve block with low dose local anesthetics on analgesia and functional outcomes following total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study
Abstract
Objective: While the safety and efficacy of peripheral nerve blocks for postoperative pain management has been established in several well controlled prospective trials, the local anesthetic (LA) concentration and volume used in these studies was associated with a significant increase muscle weakness due to motor nerve block. The purpose of the present retrospective study of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty was to assess the relative analgesic efficacy and functional outcomes of the low concentration, low volume of LA used in peripheral nerve blocks for postoperative pain management.
Methods: Twenty-four months of deidentified patient data were extracted from an electronic medical record system. All patients received opioids with or without continuous femoral and sciatic nerve block infusions for postoperative analgesia. Pain (resting and with activity), cumulative opioid and LA use were primary endpoints, participation in physical therapy (PT), muscle strength deficits and length of hospital stay (LOS) were secondary endpoints.
Results: Postoperative pain and opioid use were significantly lower in patients with peripheral nerve blocks (n = 1,329) than those with opioids alone (n = 439). There was no detectable decrease in strength associated with nerve blocks, while a significantly greater proportion of patients with nerve blocks were able to participate in PT on postoperative day 1 (96.4% vs 57.1%). These differences were not due to the impact of the surgeon per se, but whether or not the surgeon used nerve blocks for pain management. There was a small but statistically significant decrease in the average LOS in patients with blocks.
Conclusion: This analysis supports the use of low concentration, low volume of LA based peripheral nerve blocks for postoperative pain management.
Keywords: Acute Pain; Analgesic; Knee Pain; Narcotics; Regional Pain.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


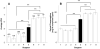
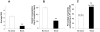
References
-
- Chelly JE, Greger J, Gebhard R, Coupe K, Clyburn TA, Buckle R, et al. Continuous femoral blocks improve recovery and outcome of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16:436–45. - PubMed
-
- Richman JM, Liu SS, Courpas G, Wong R, Rowlingson AJ, McGready J, et al. Does continuous peripheral nerve block provide superior pain control to opioids? A meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 2006;102:248–57. - PubMed
-
- Klein SM, Evans H, Nielsen KC, Tucker MS, Warner DS, Steele SM. Peripheral nerve block techniques for ambulatory surgery. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:1663–76. - PubMed
-
- Chelly JE, Ghisi D, Fanelli A. Continuous peripheral nerve blocks in acute pain management. Br J Anaesth. 2010;105(Suppl 1):i86–96. - PubMed
-
- Ilfeld BM. Continuous peripheral nerve blocks: a review of the published evidence. Anesth Analg. 2011;113:904–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

