Dual peptide conjugation strategy for improved cellular uptake and mitochondria targeting
- PMID: 25547808
- PMCID: PMC4306504
- DOI: 10.1021/bc500408p
Dual peptide conjugation strategy for improved cellular uptake and mitochondria targeting
Abstract
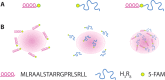
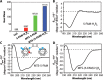
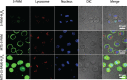
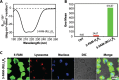
Mitochondria are critical regulators of cellular function and survival. Delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents into mitochondria is a challenging task in modern pharmacology because the molecule to be delivered needs to first overcome the cell membrane barrier and then be able to actively target the intracellular organelle. Current strategy of conjugating either a cell penetrating peptide (CPP) or a subcellular targeting sequence to the molecule of interest only has limited success. We report here a dual peptide conjugation strategy to achieve effective delivery of a non-membrane-penetrating dye 5-carboxyfluorescein (5-FAM) into mitochondria through the incorporation of both a mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) and a CPP into one conjugated molecule. Notably, circular dichroism studies reveal that the combined use of α-helix and PPII-like secondary structures has an unexpected, synergistic contribution to the internalization of the conjugate. Our results suggest that although the use of positively charged MTS peptide allows for improved targeting of mitochondria, with MTS alone it showed poor cellular uptake. With further covalent linkage of the MTS-5-FAM conjugate to a CPP sequence (R8), the dually conjugated molecule was found to show both improved cellular uptake and effective mitochondria targeting. We believe these results offer important insight into the rational design of peptide conjugates for intracellular delivery.
Figures
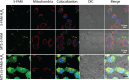
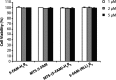
References
-
- Kroemer G.; Galluzzi L.; Brenner C. (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol. Rev. 87, 99–163. - PubMed
-
- Lin M. T.; Beal M. F. (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443, 787–795. - PubMed
-
- Fulda S.; Galluzzi L.; Kroemer G. (2010) Targeting mitochondria for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 9, 447–464. - PubMed
-
- Abadir P. M.; Foster D. B.; Crow M.; Cooke C. A.; Rucker J. J.; Jain A.; Smith B. J.; Burks T. N.; Cohn R. D.; Fedarko N. S.; Carey R. M.; O’Rourke B.; Walston J. D. (2011) Identification and characterization of a functional mitochondrial angiotensin system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 14849–14854. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muratovska A.; Lightowlers R. N.; Taylor R. W.; Turnbull D. M.; Smith R. A. J.; Wilce J. A.; Martin S. W.; Murphy M. P. (2001) Targeting peptide nucleic acid (PNA) oligomers to mitochondria within cells by conjugation to lipophilic cations: implications for mitochondrial DNA replication, expression and disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 1852–1863. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

