Combination therapy with cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25548104
- PMCID: PMC4376554
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu115
Combination therapy with cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: We performed an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of combination therapy with cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Methods: We reviewed cognitive function, activities of daily living, behavioral disturbance, global assessment, discontinuation rate, and individual side effects.
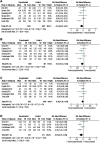
Results: Seven studies (total n=2182) were identified. Combination therapy significantly affected behavioral disturbance scores (standardized mean difference=-0.13), activity of daily living scores (standardized mean difference=-0.10), and global assessment scores (standardized mean difference=-0.15). In addition, cognitive function scores (standardized mean difference=-0.13, P=.06) exhibited favorable trends with combination therapy. The effects of combination therapy were more significant in the moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease subgroup in terms of all efficacy outcome scores. The discontinuation rate was similar in both groups, and there were no significant differences in individual side effects.
Conclusions: Combination therapy was beneficial for the treatment of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease in terms of cognition, behavioral disturbances, activities of daily living, and global assessment was well tolerated.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cholinesterase inhibitors; memantine; meta-analysis; systematic review.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures


References
-
- Ametamey SM, Bruehlmeier M, Kneifel S, Kokic M, Honer M, Arigoni M, Buck A, Burger C, Samnick S, Quack G, Schubiger PA. (2002). PET studies of 18F-memantine in healthy volunteers. Nucl Med Biol 29:227–231. - PubMed
-
- Asada T. (2012). [Prevalence of dementia in Japan: past, present and future]. Rinsho shinkeigaku 52:962–964. - PubMed
-
- Berman K, Brodaty H, Withall A, Seeher K. (2012). Pharmacologic treatment of apathy in dementia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 20:104–122. - PubMed
-
- Boada M, Arranz FJ (2013). Transdermal is better than oral: observational research of the satisfaction of caregivers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease treated with rivastigmine. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 35:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Bucks RS, Ashworth DL, Wilcock GK, Siegfried K (1996). Assessment of activities of daily living in dementia: development of the Bristol Activities of Daily Living Scale. Age Ageing 25:113–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

