Modulation of decoding fidelity by ribosomal proteins S4 and S5
- PMID: 25548247
- PMCID: PMC4336341
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.02485-14
Modulation of decoding fidelity by ribosomal proteins S4 and S5
Abstract
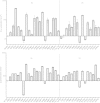
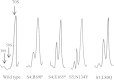
Ribosomal proteins S4 and S5 participate in the decoding and assembly processes on the ribosome and the interaction with specific antibiotic inhibitors of translation. Many of the characterized mutations affecting these proteins decrease the accuracy of translation, leading to a ribosomal-ambiguity phenotype. Structural analyses of ribosomal complexes indicate that the tRNA selection pathway involves a transition between the closed and open conformations of the 30S ribosomal subunit and requires disruption of the interface between the S4 and S5 proteins. In agreement with this observation, several of the mutations that promote miscoding alter residues located at the S4-S5 interface. Here, the Escherichia coli rpsD and rpsE genes encoding the S4 and S5 proteins were targeted for mutagenesis and screened for accuracy-altering mutations. While a majority of the 38 mutant proteins recovered decrease the accuracy of translation, error-restrictive mutations were also recovered; only a minority of the mutant proteins affected rRNA processing, ribosome assembly, or interactions with antibiotics. Several of the mutations affect residues at the S4-S5 interface. These include five nonsense mutations that generate C-terminal truncations of S4. These truncations are predicted to destabilize the S4-S5 interface and, consistent with the domain closure model, all have ribosomal-ambiguity phenotypes. A substantial number of the mutations alter distant locations and conceivably affect tRNA selection through indirect effects on the S4-S5 interface or by altering interactions with adjacent ribosomal proteins and 16S rRNA.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Another look at mutations in ribosomal protein S4 lends strong support to the domain closure model.J Bacteriol. 2015 Mar;197(6):1014-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.02579-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25548248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dinman JD, O'Connor M. 2010. Mutants that affect recoding, p 321–344. In Atkins JF, Gesteland RF (ed), Recoding: expansion of decoding rules enriches gene expression. Springer, New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

