Intestinal microbiota and type 2 diabetes: from mechanism insights to therapeutic perspective
- PMID: 25548472
- PMCID: PMC4273124
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17737
Intestinal microbiota and type 2 diabetes: from mechanism insights to therapeutic perspective
Abstract
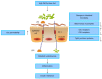
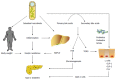
The incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is rapidly increasing worldwide. However, the pathogenesis of T2DM has not yet been well explained. Recent evidence suggests that the intestinal microbiota composition is associated with obesity and T2DM. In this review, we provide an overview about the mechanisms underlying the role of intestinal microbiota in the pathogenesis of T2DM. There is clear evidence that the intestinal microbiota influences the host through its effect on body weight, bile acid metabolism, proinflammatory activity and insulin resistance, and modulation of gut hormones. Modulating gut microbiota with the use of probiotics, prebiotics, antibiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation may have benefits for improvement in glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in the host. Further studies are required to increase our understanding of the complex interplay between intestinal microbiota and the host with T2DM. Further studies may be able to boost the development of new effective therapeutic approaches for T2DM.
Keywords: Bile-acid metabolism; Body weight; Insulin resistance; Intestinal microbiota; Intestinal microbiota modulation; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, Sixth Edition. 2013. Available from: http://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/EN_6E_Atlas_Full_0.pdf.
-
- Prevention of diabetes mellitus. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1994;844:1–100. - PubMed
-
- Berg RD. The indigenous gastrointestinal microflora. Trends Microbiol. 1996;4:430–435. - PubMed
-
- Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006;444:1022–1023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

