Post-radical prostatectomy incontinence: etiology and prevention
- PMID: 25548545
- PMCID: PMC4274175
Post-radical prostatectomy incontinence: etiology and prevention
Abstract
All patients undergoing a radical prostatectomy (RP) using any surgical approach, be it open, laparoscopic, or robotic, are at risk of developing postprostatectomy urinary incontinence. This side effect of RP has an effect on the patient's quality of life and can be associated with moderate to severe postoperative morbidity. The authors present a review of the etiology and prevention strategies of postprostatectomy urinary incontinence. Based on the current literature, the authors conclude that there is a paucity of studies that can accurately answer the exact anatomic and physiologic etiologies of postprostatectomy urinary incontinence. The aim of urologic surgeons performing RP should be to reduce the rate of postoperative incontinence rather than attempting to treat it once it has occurred. Further studies aimed at providing a detailed anatomic map of the pelvic anatomy related to continence will help to improve surgical techniques and reduce postoperative urinary incontinence following RP.
Keywords: Radical prostatectomy; Urethral length; Urinary incontinence.
Figures

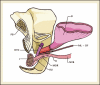
References
-
- Goluboff ET, Saidi JA, Mazer S, et al. Urinary continence after radical prostatectomy: the Columbia experience. J Urol. 1998;159:1276–1280. - PubMed
-
- Wilson LC, Gilling PJ. Post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: a review of surgical treatment options. BJU Int. 2011;107(suppl 3):7–10. - PubMed
-
- Catarin MV, Manzano GM, Nóbrega JA, et al. The role of membranous urethral afferent autonomic innervation in the continence mechanism after nerve sparing radical prostatectomy: a clinical and prospective study. J Urol. 2008;180:2527–2531. - PubMed
-
- Golomb J, Chertin B, Mor Y. Anatomy of urinary continence and neurogenic incontinence. Therapy. 2009;6:151–155.
-
- Koraitim MM. The male urethral sphincter complex revisited: an anatomical concept and its physiological correlate. J Urol. 2008;179:1683–1689. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
