Identification of new metabolites of bacterial transformation of indole by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and high performance liquid chromatography
- PMID: 25548566
- PMCID: PMC4274814
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/239641
Identification of new metabolites of bacterial transformation of indole by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and high performance liquid chromatography
Abstract
Arthrobacter sp. SPG transformed indole completely in the presence of an additional carbon source. High performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry detected indole-3-acetic acid, indole-3-glyoxylic acid, and indole-3-aldehyde as biotransformation products. This is the first report of the formation of indole-3-acetic acid, indole-3-glyoxylic acid, and indole-3-aldehyde from indole by any bacterium.
Figures

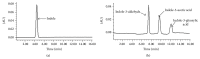
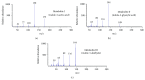

References
-
- Qu Y., Xu B., Zhang X., Ma Q., Zhou H., Kong C., Zhang Z., Zhou J. Biotransformation of indole by whole cells of recombinant biphenyl dioxygenase and biphenyl-2,3-dihydrodiol-2,3-dehydrogenase. Biochemical Engineering Journal. 2013;72:54–60. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2012.12.021. - DOI
-
- El-Shagi H., Schulte U., Zenk M. H. Specific inhibition of anthraquinone formation by amino compounds in Morinda cell cultures. Naturwissenschaften. 1984;71(5):267. doi: 10.1007/BF00441342. - DOI
-
- Sakamoto Y., Uchida M., Ichibara K. The bacterial decomposition of indole. I. Studies on its metabolic pathway by successive adaptation. Medical Journal of Osaka University. 1953;3:477–486.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

