Association of sex hormones with sexual function, vitality, and physical function of symptomatic older men with low testosterone levels at baseline in the testosterone trials
- PMID: 25548978
- PMCID: PMC4333035
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2014-3818
Association of sex hormones with sexual function, vitality, and physical function of symptomatic older men with low testosterone levels at baseline in the testosterone trials
Abstract
Context: The prevalence of sexual dysfunction, low vitality, and poor physical function increases with aging, as does the prevalence of low total and free testosterone (TT and FT) levels. However, the relationship between sex hormones and age-related alterations in older men is not clear.
Objective: To test the hypotheses that baseline serum TT, FT, estradiol (E2), and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels are independently associated with sexual function, vitality, and physical function in older symptomatic men with low testosterone levels participating in the Testosterone Trials (TTrials).
Design: Cross-sectional study of baseline measures in the TTrials.
Setting: The study was conducted at 12 sites in the United States.
Participants: The 788 TTrials participants were ≥ 65 years and had evidence of sexual dysfunction, diminished vitality, and/or mobility disability, and an average of two TT < 275 ng/dL.
Interventions: None.
Main outcome measures: Question 4 of Psychosocial Daily Questionnaire (PDQ-Q4), the FACIT-Fatigue Scale, and the 6-minute walk test.
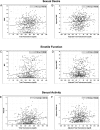
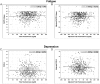
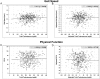
Results: Baseline serum TT and FT, but not E2 or SHBG levels had small, but statistically significant associations with validated measures of sexual desire, erectile function, and sexual activity. None of these hormones was significantly associated within or across trials with FACIT-Fatigue, PHQ-9 Depression or Physical Function-10 scores, or gait speed.
Conclusions: FT and TT levels were consistently, independently, and positively associated, albeit to a small degree, with measures of sexual desire, erectile function, and sexual activity, but not with measures of vitality or physical function in symptomatic older men with low T who qualified for the TTrials.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00799617.
Figures
References
-
- Bacon CG, Mittleman MA, Kawachi I, Giovannucci E, Glasser DB, Rimm EB. Sexual function in men older than 50 years of age: results from the health professionals follow-up study. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139(3):161–168. - PubMed
-
- Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994;151(1):54–61. - PubMed
-
- Melton LJ, 3rd, Khosla S, Crowson CS, O'Connor MK, O'Fallon WM, Riggs BL. Epidemiology of sarcopenia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2000;48(6):625–630. - PubMed
-
- Feldman HA, Longcope C, Derby CA, et al. Age trends in the level of serum testosterone and other hormones in middle-aged men: longitudinal results from the Massachusetts male aging study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(2):589–598. - PubMed
-
- Wu FC, Tajar A, Pye SR, et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis disruptions in older men are differentially linked to age and modifiable risk factors: the European Male Aging Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(7):2737–2745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

