Long term health-related quality of life in survivors of sepsis in South West Wales: an epidemiological study
- PMID: 25549097
- PMCID: PMC4280200
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116304
Long term health-related quality of life in survivors of sepsis in South West Wales: an epidemiological study
Abstract
Introduction: Survivors of sepsis report persistent problems that can last years after hospital discharge. The main aim of this study was to investigate long-term health-related quality of life in survivors of SIRS and sepsis compared with Welsh normative data, controlling for age, length of stay and pre-existing conditions. The second aim was to investigate any differences in long-term health-related quality of life specifically with the patients categorised into three groups; SIRS, uncomplicated sepsis and severe sepsis/septic shock.
Methods: A prospective study design was used in order to investigate all sepsis patients either presenting to the Emergency Department or admitted to the Intensive Care Unit of a regional trauma centre. Baseline demographics, clinical characteristics and outcomes were collected and surviving patients were sent a SF-12v2 survey at between six months to two years post-hospital discharge.
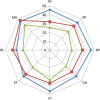
Results: Quality of life was significantly reduced in all patients when compared to local normative data (all p<0.0001). Reductions in the physical components of health-related quality of life were more pronounced in severe sepsis/septic shock patients when compared to uncomplicated sepsis and SIRS patients, when controlling for age, pre-existing conditions, hospital and ICU length of stay.
Conclusions: This is the first observational study to specifically focus on the different groups of SIRS and sepsis patients to assess long-term quality of life. Local population norms were used for comparison, rather than UK-wide norms that fail to reflect the intricacies of a country's population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Daniels R, Nutbeam T, McNamara G, Galvin C (2011) The Sepsis Six and the Surviving Sepsis Campaign Resuscitation Bundle: a prospective observational cohort study. EMJ 28:507–12. - PubMed
-
- Winters BD, Eberlein M, Leung J, Needham D, Pronovost PJ, et al. (2010) Long- term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care Med 38:1276–83. - PubMed
-
- Heyland DK, Hopman W, Coo H, Tranmer J, McColl MA (2000) Long-term health-related quality of life in survivors of sepsis. Short Form 36: A valid and reliable measure of health-related quality of life. Crit Care Med 28:3599–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

