PASTA: Ultra-Large Multiple Sequence Alignment for Nucleotide and Amino-Acid Sequences
- PMID: 25549288
- PMCID: PMC4424971
- DOI: 10.1089/cmb.2014.0156
PASTA: Ultra-Large Multiple Sequence Alignment for Nucleotide and Amino-Acid Sequences
Abstract
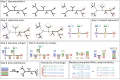
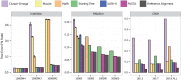
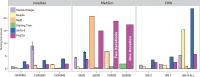
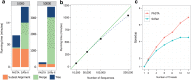
We introduce PASTA, a new multiple sequence alignment algorithm. PASTA uses a new technique to produce an alignment given a guide tree that enables it to be both highly scalable and very accurate. We present a study on biological and simulated data with up to 200,000 sequences, showing that PASTA produces highly accurate alignments, improving on the accuracy and scalability of the leading alignment methods (including SATé). We also show that trees estimated on PASTA alignments are highly accurate--slightly better than SATé trees, but with substantial improvements relative to other methods. Finally, PASTA is faster than SATé, highly parallelizable, and requires relatively little memory.
Keywords: algorithms; metagenomics; molecular evolution; multiple alignment; phylogenetic trees.
Figures
References
-
- Boisseau J., and Stanzione D.2013. TACC: Texas Advanced Computing Center. Available at: www.tacc.utexas.edu
-
- Eddy S.2009. A new generation of homology search tools based on probabilistic inference. Genome Informatics 23, 205211 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

