A key mediator, PTX3, of IKK/IκB/NF-κB exacerbates human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and dysfunction
- PMID: 25550806
- PMCID: PMC4270526
A key mediator, PTX3, of IKK/IκB/NF-κB exacerbates human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and dysfunction
Abstract
Objective: This study was performed to investigate PTX3-mediated iNOS expression and IKK/IκB/NF-κB activation in PA-induced atherosclerotic HUVECs injury model.
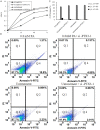
Methods: The cell viability was detected by the CCK8 assay. The cell apoptosis was assessed by annexin V-PI double-labeling staining. Expression of genes and proteins were analyzed by real-time PCR and western blotting respectively. Cells were transfected with siRNAs as a gene silencing methods.
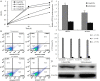
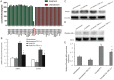
Results: PA induced cell apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in a time and dose-dependent manner. PA also induced upregulation expression of PTX3. TPCA-1, an inhibitor of IKK-2, could suppress the expression of PTX3 and phospho-IκB-α in PA-induced endothelial dysfunction cell model. We also found that transfection of cells with PTX3 siRNA reduced the expression of iNOS and NO, and protected PA-induced cell apoptosis in HUVECs.
Conclusions: PTX3 could exacerbate endothelial dysfunction, at least partially, through IKK/IκB/NF-κB activation and overexpression of iNOS and NO, and advance the development of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: HUVECs; NF-κB; PTX3; atherosclerosis; iNOS.
Figures

References
-
- Wahyudi S, Sargowo D. Green tea polyphenols inhibit oxidized LDL-induced NF-KB activation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Acta Med Indones. 2007;39:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Shi J, Sun X, Lin Y, Zou X, Li Z, Liao Y, Du M, Zhang H. Endothelial cell injury and dysfunction induced by silver nanoparticles through oxidative stress via IKK/NF-kappaB pathways. Biomaterials. 2014;35:6657–6666. - PubMed
-
- Staiger H, Staiger K, Stefan N, Wahl HG, Machicao F, Kellerer M, Haring HU. Palmitate-induced interleukin-6 expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Diabetes. 2004;53:3209–3216. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
