Influence of gag reflex on removable prosthetic restoration tolerance according to the patient section of the short form of the Gagging Problem Assessment Questionnaire
- PMID: 25551008
- PMCID: PMC4279046
- DOI: 10.4047/jap.2014.6.6.474
Influence of gag reflex on removable prosthetic restoration tolerance according to the patient section of the short form of the Gagging Problem Assessment Questionnaire
Abstract
Purpose: To assess removable prosthetic restoration tolerance according to the patient section of the short form of the Gagging Problem Assessment Questionnaire (GPA-pa SF) and the influence of gender, education level and prosthesis type and denture-related mucosal irritation on the GPA-pa SF scores before treatment and over a period of two months after prosthesis insertion.
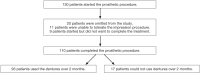
Materials and methods: 130 participants who required removable prosthesis were surveyed with a standard form that included questions regarding age, gender, education level, dental attendance, and prosthetic restoration type. Participants answered the GPA-pa SF before restoration (T0) and 1 day (T1), 2 days (T2), 15 days (T3), 1 month (T4), and 2 months (T5) after prosthesis insertion.
Results: Of the 130 participants, 110 participants completed the prosthetic restoration procedure, but only 93 of these were able to use the prosthesis over the two-month period. The mean GPA-pa SF score obtained at T0 was higher than the scores obtained at the other periods in the total of the sample. Significant difference was present between mean scores obtained at T0-T1 and T2-T3 than scores obtained at other periods (P<.05). Female participants and participants with denture-related mucosal irritation had higher GPA-pa SF scores at all time points analysed. Significant difference was present between mean GPA-pa SF scores obtained at T2-T3 than scores obtained at other periods for females and participants with denture-related mucosal irritation (P<.05). Education level and prosthesis type did not significantly influence the GPA-pa SF score at any time point analysed (P>.05).
Conclusion: GPA-pa SF scores were higher before the restoration procedure began, and decreased over time with the use of prosthesis. Gender and denture-related mucosal irritation affected the GPA-pa SF scores.
Keywords: Complete prosthesis; Gag reflex; Partial prosthesis; Pharyngeal; Prosthodontics.
References
-
- Hutton B, Feine J, Morais J. Is there an association between edentulism and nutritional state? J Can Dent Assoc. 2002;68:182–187. - PubMed
-
- Tallgren A, Lang BR, Miller RL. Longitudinal study of soft-tissue profile changes in patients receiving immediate complete dentures. Int J Prosthodont. 1991;4:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Sierpinska T, Golebiewska M, Dlugosz J, Kemona A, Laszewicz W. Connection between masticatory efficiency and pathomorphologic changes in gastric mucosa. Quintessence Int. 2007;38:31–37. - PubMed
-
- Fiske J, Davis DM, Frances C, Gelbier S. The emotional effects of tooth loss in edentulous people. Br Dent J. 1998;184:90–93. discussion 79. - PubMed
-
- Roumanas ED. The social solution-denture esthetics, phonetics, and function. J Prosthodont. 2009;18:112–115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources