Anticancer efficacy of a supramolecular complex of a 2-diethylaminoethyl-dextran-MMA graft copolymer and paclitaxel used as an artificial enzyme
- PMID: 25551057
- PMCID: PMC4273266
- DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.5.238
Anticancer efficacy of a supramolecular complex of a 2-diethylaminoethyl-dextran-MMA graft copolymer and paclitaxel used as an artificial enzyme
Abstract
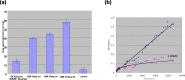
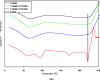
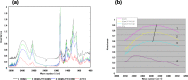
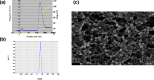
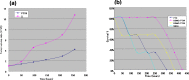
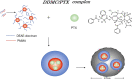
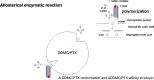
The anticancer efficacy of a supramolecular complex that was used as an artificial enzyme against multi-drug-resistant cancer cells was confirmed. A complex of diethylaminoethyl-dextran-methacrylic acid methylester copolymer (DDMC)/paclitaxel (PTX), obtained with PTX as the guest and DDMC as the host, formed a nanoparticle 50-300 nm in size. This complex is considered to be useful as a drug delivery system (DDS) for anticancer compounds since it formed a stable polymeric micelle in water. The resistance of B16F10 melanoma cells to PTX was shown clearly through a maximum survival curve. Conversely, the DDMC/PTX complex showed a superior anticancer efficacy and cell killing rate, as determined through a Michaelis-Menten-type equation, which may promote an allosteric supramolecular reaction to tubulin, in the same manner as an enzymatic reaction. The DDMC/PTX complex showed significantly higher anticancer activity compared to PTX alone in mouse skin in vivo. The median survival times of the saline, PTX, DDMC/PTX4 (particle size 50 nm), and DDMC/PTX5 (particle size 290 nm) groups were 120 h (treatment (T)/control (C), 1.0), 176 h (T/C, 1.46), 328 h (T/C, 2.73), and 280 h (T/C, 2.33), respectively. The supramolecular DDMC/PTX complex showed twice the effectiveness of PTX alone (p < 0.036). Above all, the DDMC/PTX complex is not degraded in cells and acts as an intact supramolecular assembly, which adds a new species to the range of DDS.
Keywords: artificial enzyme; diethylaminoethyl–dextran–MMA; graft copolymer; multi-drug resistance of cancer cells; paclitaxel; supramolecular complex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Medicinal facilities to B16F10 melanoma cells for distant metastasis control with a supramolecular complex by DEAE-dextran-MMA copolymer/paclitaxel.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015 Feb;5(1):38-50. doi: 10.1007/s13346-014-0213-z. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 25787338
-
A robust control system for targeting melanoma by a supermolecular DDMC/paclitaxel complex.Integr Biol (Camb). 2018 Sep 17;10(9):549-554. doi: 10.1039/c8ib00071a. Integr Biol (Camb). 2018. PMID: 30140840
-
Characteristics of DEAE-dextran-MMA graft copolymer as a nonviral gene carrier.Nanomedicine. 2007 Sep;3(3):184-91. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2007.07.002. Nanomedicine. 2007. PMID: 17765639
-
Mechanism of introduction of exogenous genes into cultured cells using DEAE-dextran-MMA graft copolymer as non-viral gene carrier.Molecules. 2009 Jul 23;14(7):2669-83. doi: 10.3390/molecules14072669. Molecules. 2009. PMID: 19633632 Free PMC article.
-
[Preparation, characterization of paclitaxel-loaded Pluronic P105 polymeric micelles and in vitro reversal of multidrug resistant tumor].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2008 Jun;43(6):640-6. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18822969 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Medicinal facilities to B16F10 melanoma cells for distant metastasis control with a supramolecular complex by DEAE-dextran-MMA copolymer/paclitaxel.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015 Feb;5(1):38-50. doi: 10.1007/s13346-014-0213-z. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 25787338
-
Engineered Polymeric Nanovector for Intracellular Peptide Delivery in Antitumor Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Sep 19;18:5343-5363. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S427536. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37746048 Free PMC article.
-
Lymph Nodes and Cancer Metastasis: New Perspectives on the Role of Intranodal Lymphatic Sinuses.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 28;18(1):51. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010051. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 28036019 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
