MicroRNA-34a functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA and suppresses angiogenesis in bladder cancer by directly targeting CD44
- PMID: 25551284
- PMCID: PMC4311467
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-014-0115-4
MicroRNA-34a functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA and suppresses angiogenesis in bladder cancer by directly targeting CD44
Abstract
Background: Metastasis have considered as an important clinical obstacle in the treatment of human cancer including bladder cancer. Post-transcriptional regulation has emerged as robust effectors of metastasis. MiRNAs are involved in cancer development and progression, acting as tumor suppressors or oncogenes. In this study, we focus on it that microRNA-34a functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA and suppress angiogenesis in bladder cancer by directly targeting CD44.
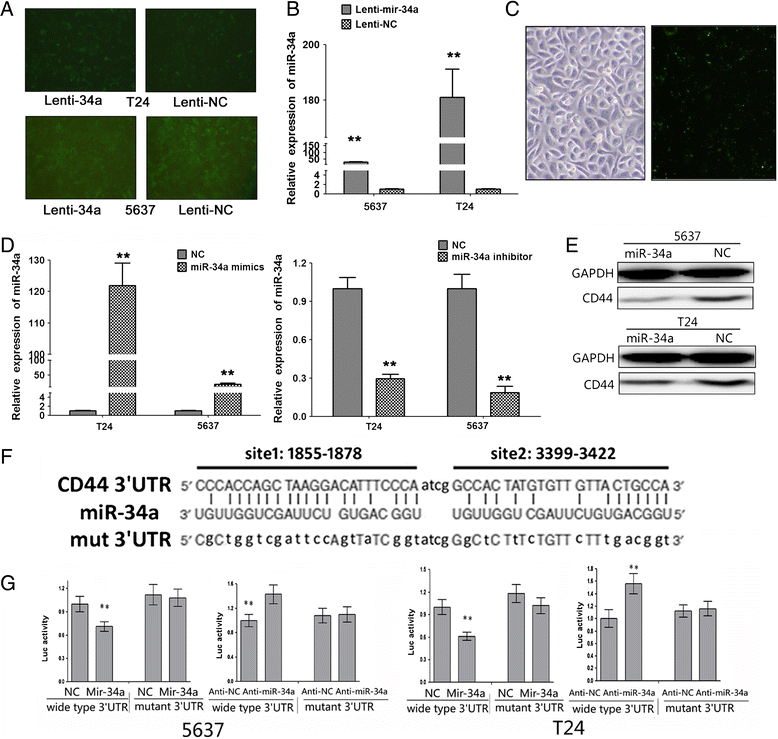
Methods: The expression of mir-34a was detected by quantitative real-time PCR. Oligonucleotide and lentivirus were used to overexpress miR-34a. Tube formation assay and transwell assay were used to examine the effect on bladder cancer tube formation, migration and invasion in vitro. Animal models were used to examine the effect on metastasis and angiogenesis in vivo. Luciferase assay was carried out to verify the precise target of miR-34a.
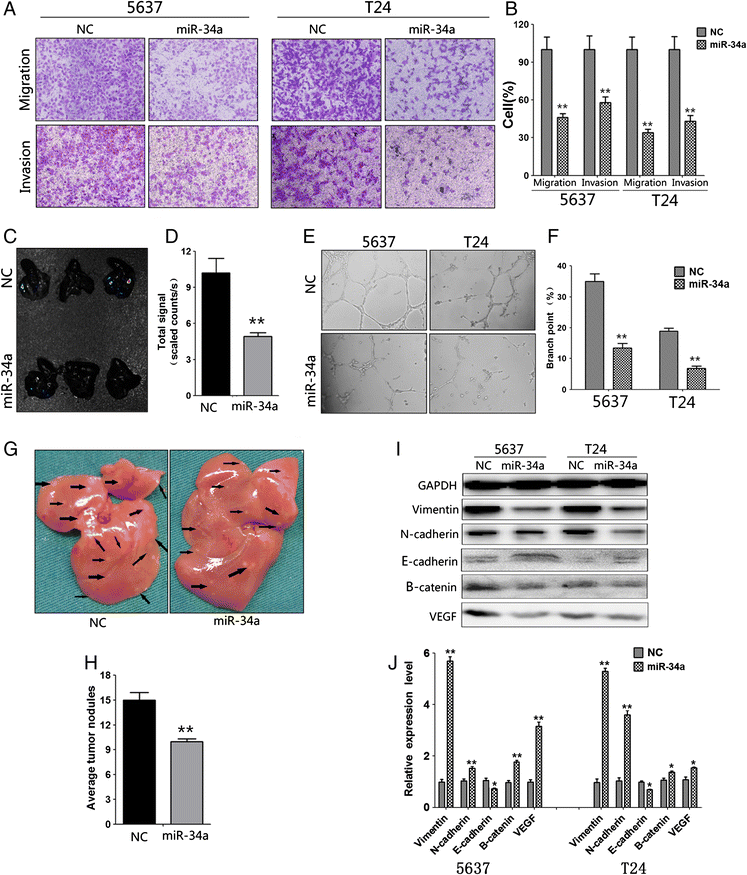
Results: We not only proved that mir-34a was significantly downregulated in bladder cancer tissues and cell lines but also that circulating miR-34a levels are reduced in bladder cancer, and their levels were positively relevance. Gain-of-function experiments investigated that increased mir-34a expression suppressed tube formation and reduced cell migration and invasion. In vivo metastasis, assays also demonstrated that overexpression of mir34a markedly inhibited bladder cancer metastasis. CD31, an endothelial cell-specific marker which stained in T24 tumors to evaluate for blood vessel density, the immunohistochemistry results showed that blood vessel quantification reduced dramatically in the T24 tumors over-expressing mir-34a. Combining with our previous studies and bioinformatics analysis, we expected that CD44 gene was a direct target of mir-34a, siRNA-mediated knockdown of CD44 partially phenocopied mir-34a overexpression suggesting that the pro-apoptotic role of mir-34a may be mediated primarily through CD44 regulation, whereas restoring the expression of CD44 attenuated the function of mir-34a in bladder cancer cells. Additionally, we identified that EMT (epithelial-mesenchymal transition) related proteins could be regulated by mir-34a which indicated that mir-34a could partially reserve EMT.
Conclusion: Our study defines a major metastasis and angiogenesis suppressive role for mir-34a, a microRNA functions as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer by directly targeting CD44, which would be helpful as a therapeutic approach to block bladder cancer metastasis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-34a suppresses invasion and metastatic in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating CD44.Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Jun;443(1-2):139-149. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3218-3. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29094237
-
MicroRNA-34a Attenuates Metastasis and Chemoresistance of Bladder Cancer Cells by Targeting the TCF1/LEF1 Axis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(1):87-98. doi: 10.1159/000491665. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30001529
-
miRNA-34a suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting CD44 in human renal carcinoma cells.J Urol. 2014 Oct;192(4):1229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.05.094. Epub 2014 May 24. J Urol. 2014. PMID: 24866595
-
Roles of MicroRNA-34a in Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, Competing Endogenous RNA Sponging and Its Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 16;20(4):861. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040861. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30781524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses metastasis of lung cancer cells by targeting the EMT regulator Sox4.Am J Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 15;6(2):127-40. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27186391 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-107 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting Axin2.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):5168-74. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191213 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory effect of compound ChlA-F on human bladder cancer cell invasion can be attributed to its blockage of SOX2 protein.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Feb;27(2):632-645. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0377-7. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31243344 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs as Anti-Angiogenic Adjuvant Therapy in Cancer: Synopsis and Potential.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 9;11:705634. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.705634. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34956857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: Their Role in Metastasis, Angiogenesis, and the Potential for Biomarker Utility in Bladder Carcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 20;13(4):891. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040891. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could miR-34a Inhibition be Used as a Tool to Overcome Drug Resistance in MCF-7 Cells Treated with Synthesized Steroidal Heterocycles?Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Mar 1;22(3):819-826. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.3.819. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33773546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kiemeney LA, Sulem P, Besenbacher S, Vermeulen SH, Sigurdsson A, Thorleifsson G, Gudbjartsson DF, Stacey SN, Gudmundsson J, Zanon C, Kostic J, Masson G, Bjarnason H, Palsson ST, Skarphedinsson OB, Gudjonsson SA, Witjes JA, Grotenhuis AJ, Verhaegh GW, Bishop DT, Sak SC, Choudhury A, Elliott F, Barrett JH, Hurst CD, de Verdier PJ, Ryk C, Rudnai P, Gurzau E, Koppova K, et al. A sequence variant at 4p16.3 confers susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer. Nat Genet. 2010;42:415–419. doi: 10.1038/ng.558. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kiemeney LA, Thorlacius S, Sulem P, Geller F, Aben KK, Stacey SN, Gudmundsson J, Jakobsdottir M, Bergthorsson JT, Sigurdsson A, Blondal T, Witjes JA, Vermeulen SH, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, Swinkels DW, Ploeg M, Cornel EB, Vergunst H, Thorgeirsson TE, Gudbjartsson D, Gudjonsson SA, Thorleifsson G, Kristinsson KT, Mouy M, Snorradottir S, Placidi D, Campagna M, Arici C, Koppova K, Gurzau E, et al. Sequence variant on 8q24 confers susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1307–1312. doi: 10.1038/ng.229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Ye Y, Kiemeney LA, Sulem P, Rafnar T, Matullo G, Seminara D, Yoshida T, Saeki N, Andrew AS, Dinney CP, Czerniak B, Zhang ZF, Kiltie AE, Bishop DT, Vineis P, Porru S, Buntinx F, Kellen E, Zeegers MP, Kumar R, Rudnai P, Gurzau E, Koppova K, Mayordomo JI, Sanchez M, Saez B, Lindblom A, de Verdier P, Steineck G, et al. Genetic variation in the prostate stem cell antigen gene PSCA confers susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer. Nat Genet. 2009;41:991–995. doi: 10.1038/ng.421. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

