ExpaRNA-P: simultaneous exact pattern matching and folding of RNAs
- PMID: 25551362
- PMCID: PMC4302096
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-014-0404-0
ExpaRNA-P: simultaneous exact pattern matching and folding of RNAs
Abstract
Background: Identifying sequence-structure motifs common to two RNAs can speed up the comparison of structural RNAs substantially. The core algorithm of the existent approach ExpaRNA solves this problem for a priori known input structures. However, such structures are rarely known; moreover, predicting them computationally is no rescue, since single sequence structure prediction is highly unreliable.
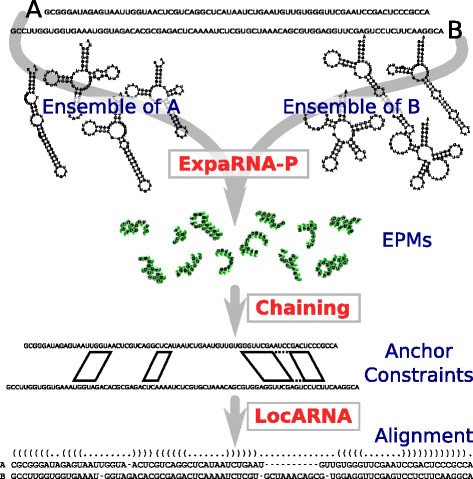
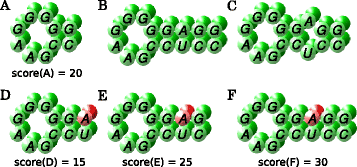
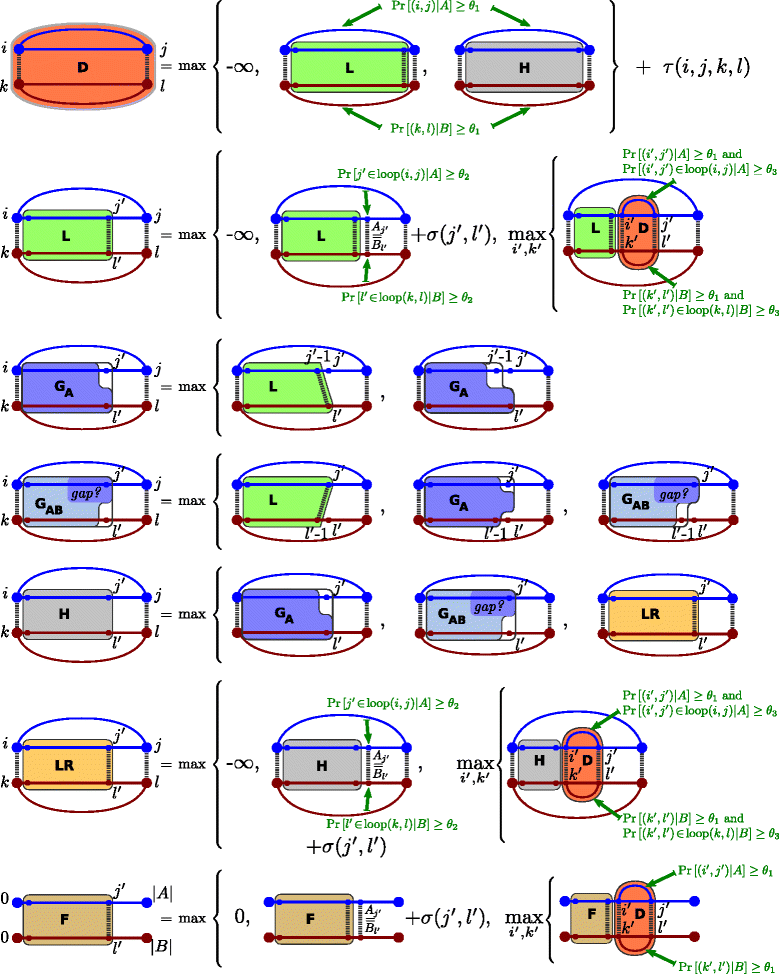
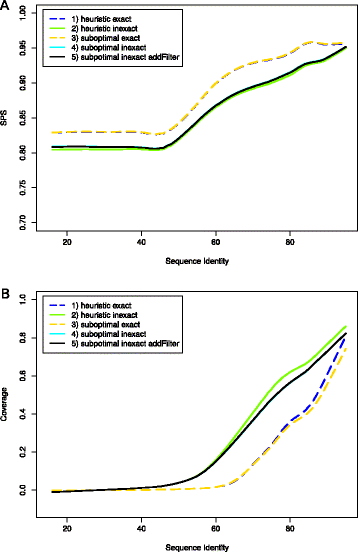
Results: The novel algorithm ExpaRNA-P computes exactly matching sequence-structure motifs in entire Boltzmann-distributed structure ensembles of two RNAs; thereby we match and fold RNAs simultaneously, analogous to the well-known "simultaneous alignment and folding" of RNAs. While this implies much higher flexibility compared to ExpaRNA, ExpaRNA-P has the same very low complexity (quadratic in time and space), which is enabled by its novel structure ensemble-based sparsification. Furthermore, we devise a generalized chaining algorithm to compute compatible subsets of ExpaRNA-P's sequence-structure motifs. Resulting in the very fast RNA alignment approach ExpLoc-P, we utilize the best chain as anchor constraints for the sequence-structure alignment tool LocARNA. ExpLoc-P is benchmarked in several variants and versus state-of-the-art approaches. In particular, we formally introduce and evaluate strict and relaxed variants of the problem; the latter makes the approach sensitive to compensatory mutations. Across a benchmark set of typical non-coding RNAs, ExpLoc-P has similar accuracy to LocARNA but is four times faster (in both variants), while it achieves a speed-up over 30-fold for the longest benchmark sequences (≈400nt). Finally, different ExpLoc-P variants enable tailoring of the method to specific application scenarios. ExpaRNA-P and ExpLoc-P are distributed as part of the LocARNA package. The source code is freely available at http://www.bioinf.uni-freiburg.de/Software/ExpaRNA-P .
Conclusions: ExpaRNA-P's novel ensemble-based sparsification reduces its complexity to quadratic time and space. Thereby, ExpaRNA-P significantly speeds up sequence-structure alignment while maintaining the alignment quality. Different ExpaRNA-P variants support a wide range of applications.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lightweight comparison of RNAs based on exact sequence-structure matches.Bioinformatics. 2009 Aug 15;25(16):2095-102. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp065. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19189979 Free PMC article.
-
LocARNA 2.0: Versatile Simultaneous Alignment and Folding of RNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2726:235-254. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3519-3_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38780734
-
SPARSE: quadratic time simultaneous alignment and folding of RNAs without sequence-based heuristics.Bioinformatics. 2015 Aug 1;31(15):2489-96. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv185. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25838465 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse RNA folding revisited: space-efficient minimum free energy structure prediction.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2016 Apr 23;11:7. doi: 10.1186/s13015-016-0071-y. eCollection 2016. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27110275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy-based RNA consensus secondary structure prediction in multiple sequence alignments.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1097:125-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-709-9_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24639158 Review.
Cited by
-
The BRaliBase dent-a tale of benchmark design and interpretation.Brief Bioinform. 2017 Mar 1;18(2):306-311. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw022. Brief Bioinform. 2017. PMID: 26984616 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and accurate structure probability estimation for simultaneous alignment and folding of RNAs with Markov chains.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2020 Nov 13;15(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13015-020-00179-w. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 33292340 Free PMC article.
-
RNAscClust: clustering RNA sequences using structure conservation and graph based motifs.Bioinformatics. 2017 Jul 15;33(14):2089-2096. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx114. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28334186 Free PMC article.
-
RNA motif search with data-driven element ordering.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 May 18;17(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1074-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27188396 Free PMC article.
-
Freiburg RNA tools: a central online resource for RNA-focused research and teaching.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 2;46(W1):W25-W29. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky329. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29788132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng J, Kapranov P, Drenkow J, Dike S, Brubaker S, Patel S, Long J, Stern D, Tammana H, Helt G, Sementchenko V, Piccolboni A, Bekiranov S, Bailey DK, Ganesh M, Ghosh S, Bell I, Gerhard DS, Gingeras TR. Transcriptional maps of 10 human chromosomes at 5-nucleotide resolution. Science. 2005;308:1149–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.1108625. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

