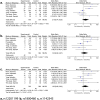
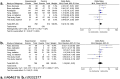
Influence of genetic variants in TPMT and COMT associated with cisplatin induced hearing loss in patients with cancer: two new cohorts and a meta-analysis reveal significant heterogeneity between cohorts
- PMID: 25551397
- PMCID: PMC4281251
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115869
Influence of genetic variants in TPMT and COMT associated with cisplatin induced hearing loss in patients with cancer: two new cohorts and a meta-analysis reveal significant heterogeneity between cohorts
Abstract
Treatment with cisplatin-containing chemotherapy regimens causes hearing loss in 40-60% of cancer patients. It has been suggested that genetic variants in the genes encoding thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) and catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) can predict the development of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and may explain interindividual variability in sensitivity to cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Two recently published studies however, sought to validate these findings and showed inconsistent results. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of polymorphisms in the TPMT and COMT genes in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Therefore we investigated two independent cohorts of 110 Dutch and 38 Spanish patients with osteosarcoma and performed a meta-analysis including all previously published studies resulting in a total population of 664 patients with cancer. With this largest meta-analysis performed to date, we show that the influence of TPMT and COMT on the development of cisplatin-induced hearing loss may be less important than previously suggested.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Knight KR, Kraemer DF, Neuwelt EA (2005) Ototoxicity in children receiving platinum chemotherapy: underestimating a commonly occurring toxicity that may influence academic and social development. J Clin Oncol 23:8588–8596. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Womer RB, Silber JH (2004) Predicting cisplaitn ototoxicity in children: the influence of age and the cumulative dose. Eur J Cancer 40:2445–2451. - PubMed
-
- Blakley BW, Gupta AK, Myers SF, Schwan S (1994) Risk factors for ototoxicity due to cisplaitn. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck surg 120:541–546. - PubMed
-
- Pan CC, Eisbruch A, Lee JS, Snorrason RM, Ten Haken RK, et al. (2005) Prospective study of inner ear radiation dose and hearing loss in head-and-neck cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61:1393–1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous