Interleukin-17A promotes functional activation of systemic sclerosis patient-derived dermal vascular smooth muscle cells by extracellular-regulated protein kinases signalling pathway
- PMID: 25551434
- PMCID: PMC4316765
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-014-0512-2
Interleukin-17A promotes functional activation of systemic sclerosis patient-derived dermal vascular smooth muscle cells by extracellular-regulated protein kinases signalling pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Dermal vascular smooth muscle cells (DVSMCs) are important for vascular wall fibrosis in microangiopathy of systemic sclerosis (SSc). T helper 17 cell-associated cytokines, particularly interleukin-17A (IL-17A), have been demonstrated to play a role in the pathogenesis of SSc. However, the effect of IL-17A on the DVSMCs in microangiopathy of SSc has not been established. In the present study, we investigated the effect of IL-17A on the SSc patient-derived DVSMCs.
Methods: DVSMCs from patients with SSc and healthy subjects were incubated using IL-17A or serum derived from patients with SSc. Subsequently, the proliferation, collagen synthesis and secretion, and migration of DVSMCs were analysed using a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), dual-luciferase reporter assay, real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and transwell assay. The protein phosphorylation of signalling pathways in the process of IL-17A-mediated DVSMC activation was investigated and validated by specific signalling pathway inhibitor.
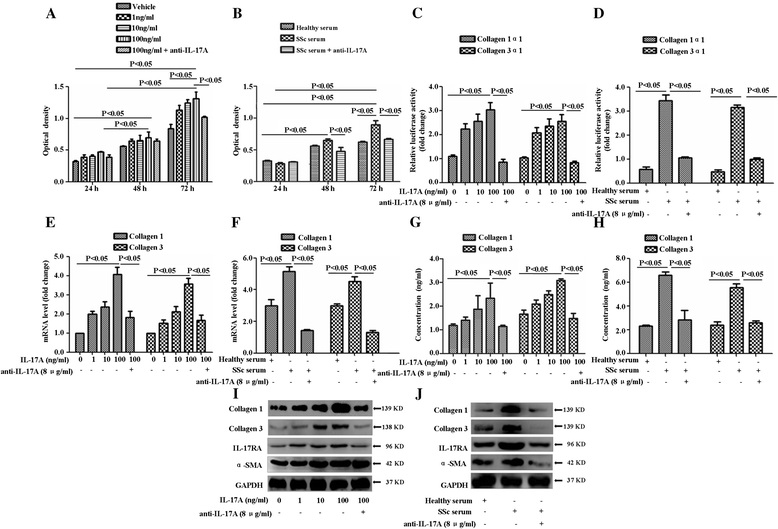
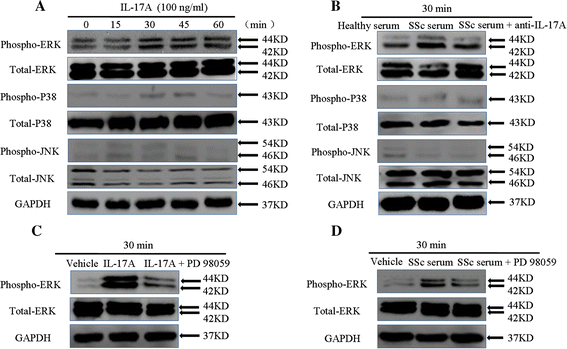
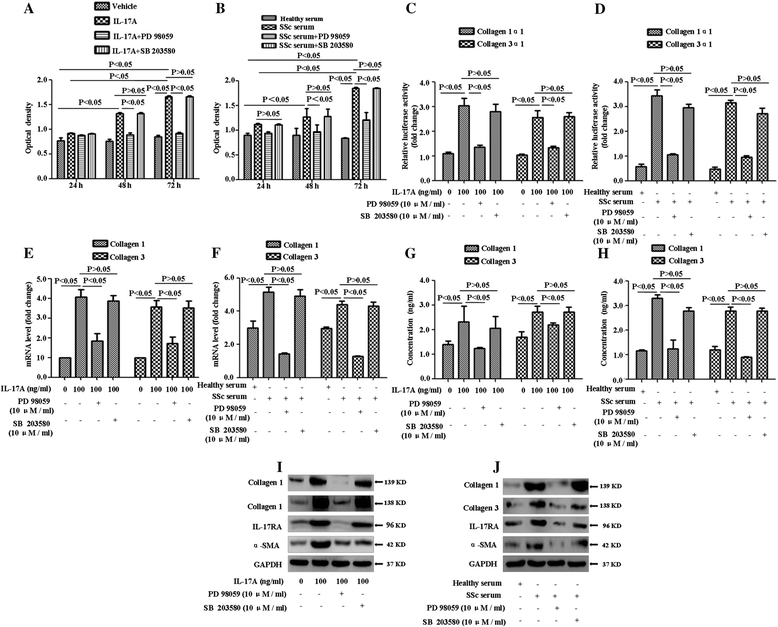
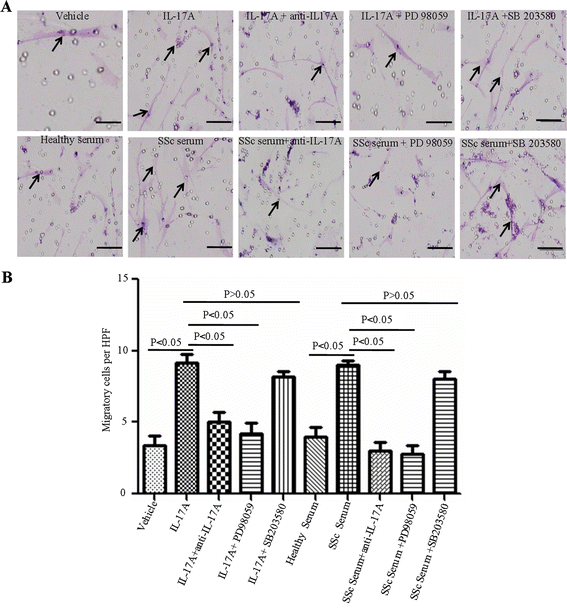
Results: IL-17A and serum from patients with SSc could promote the proliferation, collagen synthesis and secretion, and migration of DVSMCs. IL-17A neutralising antibody could inhibit the IL-17A-induced activation of DVSMCs. Additionally, IL-17A induced the activation of extracellular-regulated protein kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) in DVSMCs, and ERK1/2 inhibitor could block the IL-17A-elicited activation of DVSMCs.
Conclusions: Our results suggested that IL-17A derived from patients with SSc might induce the proliferation, collagen synthesis and secretion, and migration of DVSMCs via ERK1/2 signalling pathway, raising the likelihood that IL-17A and ERK1/2 might be promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of SSc-related vasculopathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of crosstalk between Th17 and Th9 cells on the activation of dermal vascular smooth muscle cells in systemic scleroderma and regulation of tanshinone IIA.An Bras Dermatol. 2022 Nov-Dec;97(6):716-728. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2021.11.008. Epub 2022 Sep 15. An Bras Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36117047 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA attenuates interleukin-17A-induced systemic sclerosis patient-derived dermal vascular smooth muscle cell activation via inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015 Apr;70(4):250-6. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2015(04)06. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015. PMID: 26017791 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A induces endothelial inflammation in systemic sclerosis via the ERK signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 23;8(12):e85032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085032. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376862 Free PMC article.
-
Role of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 in systemic sclerosis.Inflamm Res. 2015 Apr;64(3-4):151-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0806-0. Epub 2015 Mar 1. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 25725697 Review.
-
The Yin and Yang of IL-17 in Systemic Sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 4;13:885609. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.885609. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35603223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of crosstalk between Th17 and Th9 cells on the activation of dermal vascular smooth muscle cells in systemic scleroderma and regulation of tanshinone IIA.An Bras Dermatol. 2022 Nov-Dec;97(6):716-728. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2021.11.008. Epub 2022 Sep 15. An Bras Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36117047 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of Smooth Muscle, Striated Muscle, and the Myocardium in Scleroderma: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 9;23(19):12011. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912011. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th17 cell-derived miR-155-5p modulates interleukin-17 and suppressor of cytokines signaling 1 expression during the progression of systemic sclerosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jun;36(6):e24489. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24489. Epub 2022 May 11. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35545753 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 24;10(10):1361. doi: 10.3390/biom10101361. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32987705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Inflammatory Skin Diseases: From Bench to Bedside.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 17;11:594735. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.594735. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33281823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A, Matucci-Cerinic M, Naden RP, Medsger TA, Jr, Carreira PE, Riemekasten G, Clements PJ, Denton CP, Distler O, Allanore Y, Furst DE, Gabrielli A, Mayes MD, van Laar JM, Seibold JR, Czirjak L, Steen VD, Inanc M, Kowal-Bielecka O, Müller-Ladner U, Valentini G, Veale DJ, Vonk MC, Walker UA, Chung L. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum Dis. 2013;72:1747–1755. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204424. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

