NSK-01105, a novel sorafenib derivative, inhibits human prostate tumor growth via suppression of VEGFR2/EGFR-mediated angiogenesis
- PMID: 25551444
- PMCID: PMC4281216
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115041
NSK-01105, a novel sorafenib derivative, inhibits human prostate tumor growth via suppression of VEGFR2/EGFR-mediated angiogenesis
Abstract
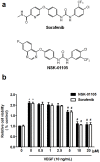
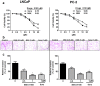
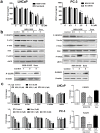
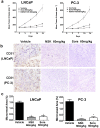
The purpose of this study is to investigate the anti-angiogenic activities of NSK-01105, a novel sorafenib derivative, in in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo models, and explore the potential mechanisms. NSK-01105 significantly inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells at non-cytotoxic concentrations as shown by wound-healing, transwell migration and endothelial cell tube formation assays, respectively. Cell viability and invasion of LNCaP and PC-3 cells were significantly inhibited by cytotoxicity assay and matrigel invasion assay. Furthermore, NSK-01105 also inhibited ex vivo angiogenesis in matrigel plug assay. Western blot analysis showed that NSK-01105 down-regulated VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) and the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Tumor volumes were significantly reduced by NSK-01105 at 60 mg/kg/day in both xenograft models. Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated a close association between inhibition of tumor growth and neovascularization. Collectively, our results suggest a role of NSK-01105 in treatment for human prostate tumors, and one of the potential mechanisms may be attributed to anti-angiogenic activities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
NSK-01105 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by blocking the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal pathways.Tumour Biol. 2015 Mar;36(3):2143-53. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2824-x. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25398692
-
SKLB1002, a novel potent inhibitor of VEGF receptor 2 signaling, inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Jul 1;17(13):4439-50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3109. Epub 2011 May 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21622720
-
Luteolin inhibits human prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052279. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300633 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-angiogenesis in prostate cancer: knocked down but not out.Asian J Androl. 2014 May-Jun;16(3):372-7. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.125903. Asian J Androl. 2014. PMID: 24759579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiangiogenic therapy in oncology: current status and future directions.Lancet. 2016 Jul 30;388(10043):518-29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01088-0. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 26853587 Review.
Cited by
-
Dissecting major signaling pathways in prostate cancer development and progression: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Feb;166:16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.07.006. Epub 2016 Jul 30. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27481707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A combination of sorafenib and nilotinib reduces the growth of castrate-resistant prostate cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Jan 8;11:179-200. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S97286. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26811677 Free PMC article.
-
Pterostilbene enhances sorafenib's anticancer effects on gastric adenocarcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(21):12525-12536. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15795. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33047871 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Channel Profiling in Prostate Cancer: Toward Cell Population-Specific Screening.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;181:39-56. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_22. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32737754 Review.
-
Potential lymphangiogenesis therapies: Learning from current antiangiogenesis therapies-A review.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(6):1769-1798. doi: 10.1002/med.21496. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29528507 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fu J, Ding Y, Huang D, Li H, Chen X (2007) The retinoid X receptor-selective ligand, LGD1069, inhibits tumor-induced angiogenesis via suppression of VEGF in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett 248:153–163. - PubMed
-
- Qi JH, Claesson-Welsh L (2001) VEGF-induced activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase is dependent on focal adhesion kinase. Exp Cell Res 263:173–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

