Subfamily-specific adaptations in the structures of two penicillin-binding proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 25551456
- PMCID: PMC4281109
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116249
Subfamily-specific adaptations in the structures of two penicillin-binding proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
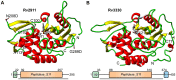
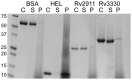
Beta-lactam antibiotics target penicillin-binding proteins including several enzyme classes essential for bacterial cell-wall homeostasis. To better understand the functional and inhibitor-binding specificities of penicillin-binding proteins from the pathogen, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, we carried out structural and phylogenetic analysis of two predicted D,D-carboxypeptidases, Rv2911 and Rv3330. Optimization of Rv2911 for crystallization using directed evolution and the GFP folding reporter method yielded a soluble quadruple mutant. Structures of optimized Rv2911 bound to phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and Rv3330 bound to meropenem show that, in contrast to the nonspecific inhibitor, meropenem forms an extended interaction with the enzyme along a conserved surface. Phylogenetic analysis shows that Rv2911 and Rv3330 belong to different clades that emerged in Actinobacteria and are not represented in model organisms such as Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Clade-specific adaptations allow these enzymes to fulfill distinct physiological roles despite strict conservation of core catalytic residues. The characteristic differences include potential protein-protein interaction surfaces and specificity-determining residues surrounding the catalytic site. Overall, these structural insights lay the groundwork to develop improved beta-lactam therapeutics for tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
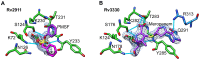
Similar articles
-
Unusual conformation of the SxN motif in the crystal structure of penicillin-binding protein A from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Mol Biol. 2010 Apr 23;398(1):54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.02.046. Epub 2010 Mar 3. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20206184 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of the transpeptidase domain of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis penicillin-binding protein PonA1 reveal potential mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.FEBS J. 2016 Jun;283(12):2206-18. doi: 10.1111/febs.13738. Epub 2016 May 25. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 27101811 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of L,D-transpeptidase LdtMt2 in complex with meropenem reveals the mechanism of carbapenem against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Cell Res. 2013 May;23(5):728-31. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.53. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23588382 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Physiological functions of D-alanine carboxypeptidases in Escherichia coli.Trends Microbiol. 2008 Jul;16(7):309-17. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Trends Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18539032 Review.
-
Penicillin-binding proteins and beta-lactam resistance.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008 Mar;32(2):361-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00095.x. Epub 2008 Jan 29. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18248419 Review.
Cited by
-
The murine metastatic microenvironment of experimental brain metastases of breast cancer differs by host age in vivo: a proteomic study.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024 Jun;41(3):229-249. doi: 10.1007/s10585-023-10233-7. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024. PMID: 37917186
-
Exploring β-lactam interactions with DacB1: unraveling optimal therapies for combating drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.mBio. 2025 Aug 13;16(8):e0137225. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01372-25. Epub 2025 Jul 10. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40637416 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure of Phosphoserine BlaC from Mycobacterium tuberculosis Inactivated by Bis(Benzoyl) Phosphate.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 2;20(13):3247. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133247. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31269656 Free PMC article.
-
β-Lactam Resistance Mechanisms: Gram-Positive Bacteria and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016 May 2;6(5):a025221. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a025221. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016. PMID: 27091943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koul A, Arnoult E, Lounis N, Guillemont J, Andries K (2011) The challenge of new drug discovery for tuberculosis. Nature 469:483–490. - PubMed
-
- Janin YL (2007) Antituberculosis drugs: ten years of research. Bioorg Med Chem 15:2479–2513. - PubMed
-
- Crick DC, Mahapatra S, Brennan PJ (2001) Biosynthesis of the arabinogalactan-peptidoglycan complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Glycobiology 11:107R–118R. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

