Genome wide identification, phylogeny and expression of zinc transporter genes in common carp
- PMID: 25551462
- PMCID: PMC4281218
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116043
Genome wide identification, phylogeny and expression of zinc transporter genes in common carp
Abstract
Background: Zinc is an essential trace element in organisms, which serves as a cofactor for hundreds of enzymes that are involved in many pivotal biological processes including growth, development, reproduction and immunity. Therefore, the homeostasis of zinc in the cell is fundamental. The zinc transporter gene family is a large gene family that encodes proteins which regulate the movement of zinc across cellular and intracellular membranes. However, studies on teleost zinc transporters are mainly limited to model species.
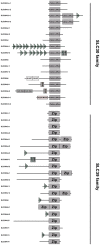
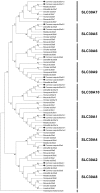
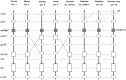
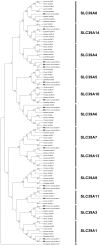
Methodology/principal findings: We identified a set of 37 zinc transporters in common carp genome, including 17 from SLC30 family (ZnT), and 20 from SLC39 family (ZIP). Phylogenetic and syntenic analysis revealed that most of the zinc transporters are highly conserved, though recent gene duplication and gene losses do exist. Through examining the copy number of zinc transporter genes across several vertebrate genomes, thirteen zinc transporters in common carp are found to have undergone the gene duplications, including SLC30A1, SLC30A2, SLC30A5, SLC30A7, SLC30A9, SLC30A10, SLC39A1, SLC39A3, SLC39A4, SLC39A5, SLC39A6, SLC39A7 and SLC39A9. The expression patterns of all zinc transporters were established in various tissues, including blood, brain, gill, heart, intestine, liver, muscle, skin, spleen and kidney, and showed that most of the zinc transporters were ubiquitously expressed, indicating the critical role of zinc transporters in common carp.
Conclusions: To some extent, examination of gene families with detailed phylogenetic or orthology analysis could verify the authenticity and accuracy of assembly and annotation of the recently published common carp whole genome sequences. The gene families are also considered as a unique source for evolutionary studies. Moreover, the whole set of common carp zinc transporters provides an important genomic resource for future biochemical, toxicological and physiological studies of zinc in teleost.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, and expression of fibroblast growth genes in common carp.Gene. 2016 Mar 10;578(2):225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.12.027. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26691502
-
Genome Wide Identification, Phylogeny, and Expression of Aquaporin Genes in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio).PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0166160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166160. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27935978 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide identification, phylogeny, and expression of bone morphogenetic protein genes in tetraploidized common carp (Cyprinus carpio).Gene. 2017 Sep 5;627:157-163. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.020. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28627438
-
The families of zinc (SLC30 and SLC39) and copper (SLC31) transporters.Curr Top Membr. 2014;73:321-55. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800223-0.00009-8. Curr Top Membr. 2014. PMID: 24745988 Review.
-
Mammalian zinc transporters.Annu Rev Nutr. 2004;24:151-72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.24.012003.132402. Annu Rev Nutr. 2004. PMID: 15189117 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of three new plant growth-promoting microbes and effects of the interkingdom interactions on plant growth and disease prevention.Plant Cell Rep. 2023 Nov;42(11):1757-1776. doi: 10.1007/s00299-023-03060-3. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Plant Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37674059
-
Identification of an IRF10 gene in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) and analysis of its function in the antiviral and antibacterial immune response.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Nov 19;16(1):450. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02674-z. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 33213475 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of Environmental Chemicals and Natural Products With ABC and SLC Transporters in the Digestive System of Aquatic Organisms.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 13;12:767766. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.767766. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35095552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vallee BL, Falchuk KH (1993) The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol Rev 73:79–118. - PubMed
-
- Fosmire GJ (1990) Zinc toxicity. Am J Clin Nutr 51:225–227. - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Tepaamorndech S (2013) The SLC30 family of zinc transporters–A review of current understanding of their biological and pathophysiological roles. Mol Aspects Med 34:548–560. - PubMed
-
- Eide DJ (2004) The SLC39 family of metal ion transporters. Pflügers Archiv 447:796–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

