Up-regulation of miR-9 expression predicate advanced clinicopathological features and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25552204
- PMCID: PMC4348155
- DOI: 10.1186/s13000-014-0228-2
Up-regulation of miR-9 expression predicate advanced clinicopathological features and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small (19-24 nt long) noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression in a sequence specific manner. An increasing association between miRNA and cancer has been recently reported. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as the fifth most common cancer and the most common cause of death in men, has become the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. In this study, we investigated the miR-9 expression in HCC to evaluate their value in prognosis of this tumor.
Methods: The expression of miR-9 in matched normal and tumor tissues of HCC was evaluated using a quantitative real-time RT-PCR. A Kaplan-Meier survival curve was generated following a log-rank test.
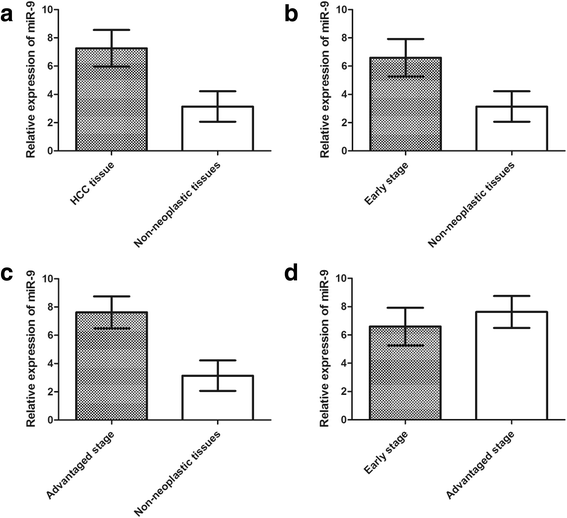
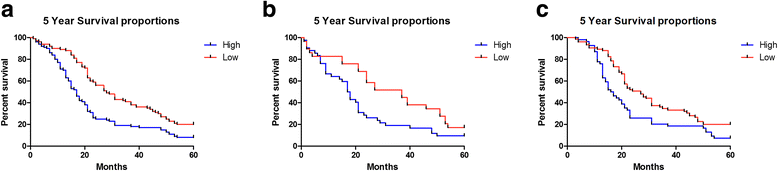
Results: It was observed that miR-9 expression was upregulated in HCC tissues compared with noncancerous liver tissues (7.26 ± 1.30 vs. 3.14 ± 1.08, P < 0.001). The up-regulation of miR-9 in HCC cancer tissues was also significantly correlated with aggressive clinicopathological features. We found that the patients with high miR-9 expression have a higher tumor staging (P = 0.0389) and are in higher risk of venous infiltration (P < 0.0001). Moreover, the results of Kaplan-Meier analyses showed that HCC patients with the high miR-9 expression tend to have shorter overall survival (P < 0.0001). The multivariate analysis clearly indicated that the high miR-9 expression in biopsy samples may be considered as an independent prognostic factor in HCC for decreased survival (4.28; 95%CI, 2.77-7.23, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our data indicate the potential of miR-9 as a novel prognostic biomarker for HCC. Large well-designed studies with diverse populations and functional evaluations are warranted to confirm and extend our findings.
Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/13000_2014_228.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Up-Regulation of miR-21 Expression Predicate Advanced Clinicopathological Features and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2016 Jan;22(1):161-7. doi: 10.1007/s12253-015-9979-7. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Pathol Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 26453197
-
Neuron-glial antigen 2 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts poor prognosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 7;21(21):6649-59. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6649. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26074703 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of miR-21 predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):7234-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261620 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker MicroRNAs for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Functional Survey and Comparison.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 5;6:38311. doi: 10.1038/srep38311. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27917899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs involved with hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Oncol Rep. 2015 Dec;34(6):2811-20. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4275. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26398882 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional microRNA high throughput screening reveals miR-9 as a central regulator of liver oncogenesis by affecting the PPARA-CDH1 pathway.BMC Cancer. 2015 Jul 24;15:542. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1562-9. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26206264 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-32 Regulates Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting ADAMTS9 and Affects Its Prognosis.Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2018 Nov 5;24:177-187. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.910522. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2018. PMID: 30393368 Free PMC article.
-
Stepwise analysis of MIR9 loci identifies miR-9-5p to be involved in Oestrogen regulated pathways in breast cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 27;7:45283. doi: 10.1038/srep45283. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28345661 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of microRNA-9 in Various Cancers: a Meta-analysis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2017 Jul;23(3):573-582. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0148-4. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Pathol Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 27844330 Free PMC article.
-
Myc target gene, long intergenic noncoding RNA, Linc00176 in hepatocellular carcinoma regulates cell cycle and cell survival by titrating tumor suppressor microRNAs.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 4;37(1):75-85. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.312. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28869604
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

