Procyanidin B2 3,3″-di-O-gallate inhibits endothelial cells growth and motility by targeting VEGFR2 and integrin signaling pathways
- PMID: 25552257
- PMCID: PMC4586152
- DOI: 10.2174/1568009614666141229102254
Procyanidin B2 3,3″-di-O-gallate inhibits endothelial cells growth and motility by targeting VEGFR2 and integrin signaling pathways
Abstract
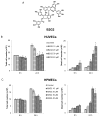
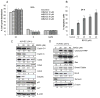
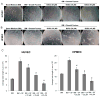
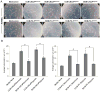
Targeting angiogenesis, one of the hallmarks of carcinogenesis, using non-toxic phytochemicals has emerged as a translational opportunity for angioprevention and to control advanced stages of malignancy. Herein, we investigated the inhibitory effects and associated mechanism/s of action of Procyanidin B2-3,3″-di- O-gallate (B2G2), a major component of grape seed extract, on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and human prostate microvascular endothelial cells (HPMECs). Our results showed that B2G2 (10-40 μM) inhibits growth and induces death in both HUVECs and HPMECs. Additional studies revealed that B2G2 causes a G1 arrest in cell cycle progression of HUVECs by down-regulating cyclins (D1 and A), CDKs (Cdk2 and Cdc2) and Cdc25c phosphatase and up-regulating CDK inhibitors (p21 and p27) expression. B2G2 also induced strong apoptotic death in HUVECs through increasing p53, Bax and Smac/Diablo expression while decreasing Bcl-2 and survivin levels. Additionally, B2G2 inhibited the growth factors-induced capillary tube formation in HUVECs and HPMECs. Interestingly, conditioned media (CCM) from prostate cancer (PCA) cells (LNCaP and PC3) grown under normoxic (~21% O2) and hypoxic (1% O2) conditions significantly enhanced the tube formation in HUVECs, which was compromised in presence of conditioned media from B2G2-treated PCA cells. B2G2 also inhibited the motility and invasiveness of both HUVECs and HPMECs. Mechanistic studies showed that B2G2 targets VEGFR2/PI3K/Akt and integrin signaling molecules which are important for endothelial cells survival, proliferation, tube formation and motility. Overall, we report that B2G2 inhibits several attributes of angiogenesis in cell culture; therefore, it warrants further investigation for efficacy for angioprevention and cancer control.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were identified by any authors of this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential effect of grape seed extract and its active constituent procyanidin B2 3,3″-di-O-gallate against prostate cancer stem cells.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Jul;58(7):1105-1117. doi: 10.1002/mc.22995. Epub 2019 Mar 3. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 30828884 Free PMC article.
-
Procyanidin B2 3,3″-di-O-gallate induces oxidative stress-mediated cell death in prostate cancer cells via inhibiting MAP kinase phosphatase activity and activating ERK1/2 and AMPK.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Jan;57(1):57-69. doi: 10.1002/mc.22731. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 28876465 Free PMC article.
-
Procyanidin B2 3,3(″)-di-O-gallate, a biologically active constituent of grape seed extract, induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells via targeting NF-κB, Stat3, and AP1 transcription factors.Nutr Cancer. 2014;66(4):736-46. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2013.783602. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Nutr Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24191894 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing traffic on vascular routes.Mol Aspects Med. 2011 Apr;32(2):112-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.04.003. Epub 2011 Apr 23. Mol Aspects Med. 2011. PMID: 21536065 Review.
-
Integrins and cancer.Oncology (Williston Park). 2007 Aug;21(9 Suppl 3):13-20. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007. PMID: 17927026 Review.
Cited by
-
PKM2 is the target of proanthocyanidin B2 during the inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 17;38(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1194-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31101057 Free PMC article.
-
Construction Of High Loading Natural Active Substances Nanoplatform and Application in Synergistic Tumor Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Jun 15;17:2647-2659. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S364108. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35730051 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening in search of novel Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitors.J Mol Model. 2019 Jun 6;25(7):179. doi: 10.1007/s00894-019-4047-y. J Mol Model. 2019. PMID: 31172362
-
Proanthocyanidins of Natural Origin: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications for Lipid Disorder and Aging-Associated Diseases.Adv Nutr. 2019 May 1;10(3):464-478. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy118. Adv Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30926997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Periostin, a signal transduction intermediate in TGF-β-induced EMT in U-87MG human glioblastoma cells, and its inhibition by anthocyanidins.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 24;9(31):22023-22037. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25153. eCollection 2018 Apr 24. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29774119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Seminars in oncology. 2002;29(6 Suppl 16):15–18. - PubMed
-
- Gacche RN, Meshram RJ. Angiogenic factors as potential drug target: Efficacy and limitations of anti-angiogenic therapy. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2014;1846(1):161–179. - PubMed
-
- Naumov GN, Akslen LA, Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in human tumor dormancy: animal models of the angiogenic switch. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(16):1779–1787. - PubMed
-
- Naumov GN, Folkman J, Straume O. Tumor dormancy due to failure of angiogenesis: role of the microenvironment. Clinical & experimental metastasis. 2009;26(1):51–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

