Genome engineering using a synthetic gene circuit in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 25552415
- PMCID: PMC4381049
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1380
Genome engineering using a synthetic gene circuit in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
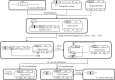
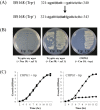
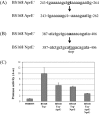
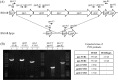
Genome engineering without leaving foreign DNA behind requires an efficient counter-selectable marker system. Here, we developed a genome engineering method in Bacillus subtilis using a synthetic gene circuit as a counter-selectable marker system. The system contained two repressible promoters (B. subtilis xylA (Pxyl) and spac (Pspac)) and two repressor genes (lacI and xylR). Pxyl-lacI was integrated into the B. subtilis genome with a target gene containing a desired mutation. The xylR and Pspac-chloramphenicol resistant genes (cat) were located on a helper plasmid. In the presence of xylose, repression of XylR by xylose induced LacI expression, the LacIs repressed the Pspac promoter and the cells become chloramphenicol sensitive. Thus, to survive in the presence of chloramphenicol, the cell must delete Pxyl-lacI by recombination between the wild-type and mutated target genes. The recombination leads to mutation of the target gene. The remaining helper plasmid was removed easily under the chloramphenicol absent condition. In this study, we showed base insertion, deletion and point mutation of the B. subtilis genome without leaving any foreign DNA behind. Additionally, we successfully deleted a 2-kb gene (amyE) and a 38-kb operon (ppsABCDE). This method will be useful to construct designer Bacillus strains for various industrial applications.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A versatile mini-mazF-cassette for marker-free targeted genetic modification in Bacillus subtilis.J Microbiol Methods. 2013 Nov;95(2):207-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.07.020. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Microbiol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23911571
-
Development and characterization of a xylose-dependent system for expression of cloned genes in Bacillus subtilis: conditional complementation of a teichoic acid mutant.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Jan;67(1):403-10. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.1.403-410.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11133472 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Bacillus subtilis xyl operon is repressed at the level of transcription and is induced by xylose.J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3102-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3102-3109.1988. J Bacteriol. 1988. PMID: 2454911 Free PMC article.
-
High molecular weight DNA assembly in vivo for synthetic biology applications.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017 May;37(3):277-286. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2016.1141394. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 26863154 Review.
-
Bacterial epigenetics and its implication for agriculture, probiotics development, and biotechnology design.Biotechnol Adv. 2024 Oct;75:108414. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108414. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Biotechnol Adv. 2024. PMID: 39019123 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronicle of a Soil Bacterium: Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 as a Tiny Guardian of Plant and Human Health.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 15;10:467. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00467. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30930873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances on systems metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis as a chassis cell.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 29;5(4):245-251. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2020.07.005. eCollection 2020 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32775709 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Factory Engineering of Undomesticated Bacillus Strains Using a Modified Integrative and Conjugative Element for Efficient Plasmid Delivery.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 26;13:802040. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.802040. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35558120 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus integrative plasmid system combining a synthetic gene circuit for efficient genetic modifications of undomesticated Bacillus strains.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Dec 14;21(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01989-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36517844 Free PMC article.
-
Fragment Exchange Plasmid Tools for CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Integration and Protease Production in Bacillus subtilis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Dec 17;87(1):e02090-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02090-20. Print 2020 Dec 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33097498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schallmey M., Singh A., Ward O.P. Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004;50:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Schumann W. Production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2007;62:137–189. - PubMed
-
- Pohl S., Harwood C.R. Heterologous protein secretion by Bacillus species from the cradle to the grave. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2010;73:1–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

