Neural biomarkers for assessing different types of imagery in pictorial health warning labels for cigarette packaging: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 25552613
- PMCID: PMC4281542
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006411
Neural biomarkers for assessing different types of imagery in pictorial health warning labels for cigarette packaging: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
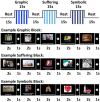
Objective: Countries around the world have increasingly adopted pictorial health warning labels (HWLs) for tobacco packages to warn consumers about smoking-related risks. Research on how pictorial HWLs work has primarily analysed self-reported responses to HWLs; studies at the neural level comparing the brain's response to different types of HWLs may provide an important complement to prior studies, especially if self-reported responses are systematically biased. In this study we characterise the brain's response to three types of pictorial HWLs for which prior self-report studies indicated different levels of efficacy.
Methods: Current smokers rated pictorial HWLs and then observed the same HWLs during functional MRI (fMRI) scanning. Fifty 18-50-year-old current adult smokers who were free from neurological disorders were recruited from the general population and participated in the study. Demographics, smoking-related behaviours and self-reported ratings of pictorial HWL stimuli were obtained prior to scanning. Brain responses to HWLs were assessed using fMRI, focusing on a priori regions of interest.
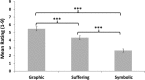
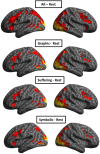
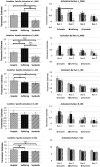
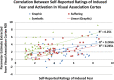
Results: Pictorial HWL stimuli elicited activation in a broad network of brain areas associated with visual processing and emotion. Participants who rated the stimuli as more emotionally arousing also showed greater neural responses at these sites.
Conclusions: Self-reported ratings of pictorial HWLs are correlated with neural responses in brain areas associated with visual and emotional processing. Study results cross-validate self-reported ratings of pictorial HWLs and provide insights into how pictorial HWLs are processed.
Keywords: PUBLIC HEALTH.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linking mass media campaigns to pictorial warning labels on cigarette packages: a cross-sectional study to evaluate effects among Mexican smokers.Tob Control. 2013 May;22(e1):e57-65. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2011-050282. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Tob Control. 2013. PMID: 22752271
-
Over-Time Impacts of Pictorial Health Warning Labels and their Differences across Smoker Subgroups: Results from Adult Smokers in Canada and Australia.Nicotine Tob Res. 2018 Jun 7;20(7):888-896. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntx134. Nicotine Tob Res. 2018. PMID: 28637294 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of pictorial health warning labels on smoking beliefs and perceptions among waterpipe smokers: an online randomised cross-over experimental study.Tob Control. 2023 Nov;32(6):715-722. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2021-057202. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Tob Control. 2023. PMID: 35444030 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Perceived effectiveness of pictorial health warnings on changes in smoking behaviour in Asia: a literature review.BMC Public Health. 2018 Oct 11;18(1):1165. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-6072-7. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30305061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of health warning labels on selection and consumption of food and alcohol products: systematic review with meta-analysis.Health Psychol Rev. 2021 Sep;15(3):430-453. doi: 10.1080/17437199.2020.1780147. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Health Psychol Rev. 2021. PMID: 32515697 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Young Adult Smokers' Neural Response to Graphic Cigarette Warning Labels.Addict Behav Rep. 2016 Jun 1;3:28-32. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2016.02.001. Addict Behav Rep. 2016. PMID: 27019865 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of smoking status on neuronal responses to graphic cigarette warning labels.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 20;13(9):e0201360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201360. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30235214 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Brain Responses to Anti-Smoking Health Warnings In Youth.Curr Addict Rep. 2018 Sep;5(3):372-378. doi: 10.1007/s40429-018-0221-z. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Curr Addict Rep. 2018. PMID: 31396471 Free PMC article.
-
Neural mechanisms underlying visual attention to health warnings on branded and plain cigarette packs.Addiction. 2017 Apr;112(4):662-672. doi: 10.1111/add.13699. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Addiction. 2017. PMID: 27886656 Free PMC article.
-
Neural response to pictorial health warning labels can predict smoking behavioral change.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Nov;11(11):1802-1811. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsw087. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27405615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. WHO framwork convention. 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
