Early Parkinson's disease symptoms in α-synuclein transgenic monkeys
- PMID: 25552648
- PMCID: PMC4375423
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu748
Early Parkinson's disease symptoms in α-synuclein transgenic monkeys
Abstract
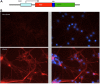
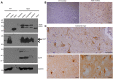
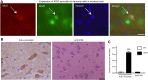
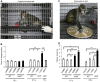
Parkinson's disease (PD) is an age-dependent neurodegenerative disease that can be caused by genetic mutations in α-synuclein (α-syn) or duplication of wild-type α-syn; PD is characterized by the deposition of α-syn aggregates, indicating a gain of toxicity from accumulation of α-syn. Although the major neuropathologic feature of PD is the degeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra, non-motor symptoms including anxiety, cognitive defect and sleep disorder precede the onset of motor impairment, and many clinical symptoms of PD are not caused by degeneration of DA neurons. Non-human primate models of PD are important for revealing the early pathology in PD and identifying effective treatments. We established transgenic PD rhesus monkeys that express mutant α-syn (A53T). Six transgenic A53T monkeys were produced via lentiviral vector expressing A53T in fertilized monkey eggs and subsequent embryo transfer to surrogates. Transgenic A53T is expressed in the monkey brain and causes age-dependent non-motor symptoms, including cognitive defects and anxiety phenotype, without detectable sleeping disorders. The transgenic α-syn monkeys demonstrate the specific early symptoms caused by mutant α-syn and provide insight into treatment of early PD.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intracerebral Administration of a Ligand-ASO Conjugate Selectively Reduces α-Synuclein Accumulation in Monoamine Neurons of Double Mutant Human A30P*A53T*α-Synuclein Transgenic Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 13;22(6):2939. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062939. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805843 Free PMC article.
-
alpha -Synucleinopathy and selective dopaminergic neuron loss in a rat lentiviral-based model of Parkinson's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Aug 6;99(16):10813-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152339799. Epub 2002 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12122208 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Synuclein transgenic mice, h-α-SynL62, display α-Syn aggregation and a dopaminergic phenotype reminiscent of Parkinson's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Feb 26;339:153-168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.11.025. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29180135
-
Interaction between Neuromelanin and Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease.Biomolecules. 2015 Jun 5;5(2):1122-42. doi: 10.3390/biom5021122. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26057626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parkinson's disease and alpha synuclein: is Parkinson's disease a prion-like disorder?Mov Disord. 2013 Jan;28(1):31-40. doi: 10.1002/mds.25373. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 23390095 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutant alpha-synuclein causes age-dependent neuropathology in monkey brain.J Neurosci. 2015 May 27;35(21):8345-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0772-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26019347 Free PMC article.
-
Gene editing monkeys: Retrospect and outlook.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 8;10:913996. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.913996. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36158194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opportunities and challenges in modeling human brain disorders in transgenic primates.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Aug 26;19(9):1123-30. doi: 10.1038/nn.4362. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27571191
-
Generation and Breeding of EGFP-Transgenic Marmoset Monkeys: Cell Chimerism and Implications for Disease Modeling.Cells. 2021 Feb 27;10(3):505. doi: 10.3390/cells10030505. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33673402 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically modified large animal models for investigating neurodegenerative diseases.Cell Biosci. 2021 Dec 21;11(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00729-8. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34933675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hardy J., Cai H., Cookson M.R., Gwinn-Hardy K., Singleton A. (2006) Genetics of Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol., 60, 389–398. - PubMed
-
- Trojanowski J.Q., Lee V.M. (1998) Aggregation of neurofilament and alpha-synuclein proteins in Lewy bodies: implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease and Lewy body dementia. Arch. Neurol., 55, 151–152. - PubMed
-
- Spillantini M.G., Schmidt M.L., Lee V.M., Trojanowski J.Q., Jakes R., Goedert M. (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature, 388, 839–840. - PubMed
-
- Singleton A.B. (2005) Altered alpha-synuclein homeostasis causing Parkinson's disease: the potential roles of dardarin. Trends Neurosci., 28, 416–421. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri K.R., Schapira A.H. (2009) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease: dopaminergic pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Neurol., 8, 464–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

