Genetic knockdown of estrogen receptor-alpha in the subfornical organ augments ANG II-induced hypertension in female mice
- PMID: 25552661
- PMCID: PMC4360069
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00406.2014
Genetic knockdown of estrogen receptor-alpha in the subfornical organ augments ANG II-induced hypertension in female mice
Abstract
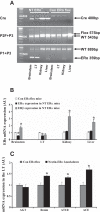
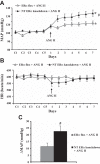
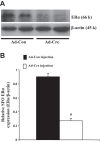
The present study tested the hypotheses that 1) ERα in the brain plays a key role in the estrogen-protective effects against ANG II-induced hypertension, and 2) that the subfornical organ (SFO) is a key site where ERα mediates these protective actions. In this study, a "floxed" ERα transgenic mouse line (ERα(flox)) was used to create models in which ERα was knocked down in the brain or just in the SFO. Female mice with ERα ablated in the nervous system (Nestin-ERα(-) mice) showed greater increases in blood pressure (BP) in response to ANG II. Furthermore, females with ERα knockdown specifically in the SFO [SFO adenovirus-Cre (Ad-Cre) injected ERα(flox) mice] also showed an enhanced pressor response to ANG II. Immunohistochemical (IHC), RT-PCR, and Western blot analyses revealed a marked reduction in the expression of ERα in nervous tissues and, in particular, in the SFO. These changes were not present in peripheral tissues in Nestin-ERα(-) mice or Ad-Cre-injected ERα(flox) mice. mRNA expression of components of the renin-angiotensin system in the lamina terminalis were upregulated in Nestin-ERα(-) mice. Moreover, ganglionic blockade on day 7 after ANG II infusions resulted in a greater reduction of BP in Nestin-ERα(-) mice or SFO Ad-Cre-injected mice, suggesting that knockdown of ERα in the nervous system or the SFO alone augments central ANG II-induced increase in sympathetic tone. The results indicate that interfering with the action of estrogen on SFO ERα is sufficient to abolish the protective effects of estrogen against ANG II-induced hypertension.
Keywords: ANG II; blood pressure; estrogen receptor-α; nervous system; subfornical organ.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Antonson P, Omoto Y, Humire P, Gustafsson JÅ. Generation of ERα-floxed and knockout mice using the Cre/LoxP system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 424: 710–716, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Ciriello J, Roder S. 17β-Estradiol alters the response of subfornical organ neurons that project to supraoptic nucleus to plasma angiotensin II and hypernatremia. Brain Res 1526: 54–64, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Dean SA, Tan J, O'Brien ER, Leenen FH. 17 β-estradiol downregulates tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme and ANG II type 1 receptor in female rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288: R759–R766, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Dubois NC, Hofmann D, Kaloulis K, Bishop JM, Trumpp A. Nestin-Cre transgenic mouse line Nes-Cre1 mediates highly efficient Cre/LoxP mediated recombination in the nervous system, kidney, and somite-derived tissues. Genesis 44: 355–360, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

