An antiaging skin care system containing alpha hydroxy acids and vitamins improves the biomechanical parameters of facial skin
- PMID: 25552908
- PMCID: PMC4277239
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S75439
An antiaging skin care system containing alpha hydroxy acids and vitamins improves the biomechanical parameters of facial skin
Abstract
Background: The demand for antiaging products has dramatically increased in recent years, driven by an aging population seeking to maintain the appearance of youth. This study investigates the effects of an antiaging skin care system containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) in conjunction with vitamins B3, C, and E on the biomechanical parameters of facial skin.
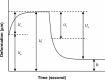
Methods: Fifty two volunteers followed an antiaging skin care regimen comprising of cleanser, eye cream, day moisturizer, and night moisturizer for 21 days. Wrinkle depth (Ry ) and skin roughness (Ra ) were measured by skin surface profilometry of the crow's feet area, and skin elasticity parameters R2 (gross elasticity), R5 (net elasticity), R6 (viscoelastic portion), and R7 (recovery after deformation) were determined for facial skin by cutometer, preapplication and after 7, 14, and 21 days. Volunteers also completed a self-assessment questionnaire.
Results: Compared to baseline, Ry and Ra significantly improved by 32.5% (P<0.0001) and 42.9% (P<0.0001), respectively, after 21 days of antiaging skin care treatment. These results were observed by the volunteers with 9 out of 10 discerning an improvement in skin texture and smoothness. Compared to baseline, R2 and R5 significantly increased by 15.2% (P<0.0001) and 12.5% (P=0.0449), respectively, while R6 significantly decreased by 17.7% (P<0.0001) after 21 days. R7 increased by 9.7% after 21 days compared to baseline but this was not significant over this time period.
Conclusion: An antiaging skin care system containing AHAs and vitamins significantly improves the biomechanical parameters of the skin including wrinkles and skin texture, as well as elasticity without significant adverse effects.
Keywords: alpha hydroxy acids; antiaging; cutometer; nicotinamide; profilometry; vitamin C; vitamin E.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Use of formulations for sensitive skin improves the visible signs of aging, including wrinkle size and elasticity.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019 Jun 6;12:415-425. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S212240. eCollection 2019. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31239745 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of topical antiaging creams in the management of lateral canthal lines.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Mar;19(3):694-704. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13062. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31350814 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
How much related to skin wrinkles between facial and body site? Age-related changes in skin wrinkle on the knee assessed by skin bioengineering techniques.Skin Res Technol. 2016 Feb;22(1):69-74. doi: 10.1111/srt.12230. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Skin Res Technol. 2016. PMID: 25801732
-
The use of polyhydroxy acids (PHAs) in photoaged skin.Cutis. 2004 Feb;73(2 Suppl):3-13. Cutis. 2004. PMID: 15002656 Review.
-
Mannose-6-phosphate complex and improvement in biomechanical properties of the skin.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021 Jun;20(6):1598-1610. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14000. Epub 2021 Mar 10. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33580613 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Characterization and Bioactivity of a Titanium(IV)-Oxo Complex Stabilized by Mandelate Ligands.Molecules. 2024 Apr 11;29(8):1736. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081736. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675556 Free PMC article.
-
Potential anti-ageing effects of probiotic-derived conditioned media on human skin cells.Acta Pharm. 2022 Apr 13;72(3):359-374. doi: 10.2478/acph-2022-0027. Print 2022 Sep 1. Acta Pharm. 2022. PMID: 36651546
-
Oxidative stress in aging human skin.Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 21;5(2):545-89. doi: 10.3390/biom5020545. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 25906193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Nutritional Elements in Skin Homeostasis: A Review.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 3;15(6):808. doi: 10.3390/biom15060808. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Orally Administered Collagen Peptides from Bovine Bone on Skin Aging in Chronologically Aged Mice.Nutrients. 2017 Nov 3;9(11):1209. doi: 10.3390/nu9111209. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29099747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Langton AK, Sherratt MJ, Griffiths CEM, Watson REB. A new wrinkle on old skin: the role of elastic fibres in skin ageing. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010;32(5):330–339. - PubMed
-
- Montagna W, Kirchner S, Carlisle K. Histology of sun-damaged human-skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(5 Pt 1):907–918. - PubMed
-
- Warren R, Gartstein V, Kligman AM, et al. Age, sunlight, and facial skin: a histologic and quantitative study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25(5 Pt 1):751–760. - PubMed
-
- Rokhsar CK, Lee S, Fitzpatrick RE. Review of photorejuvenation: devices, cosmeceuticals, or both? Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(9 Pt 2):1166–1178. - PubMed
-
- Cosmeceuticals . US Industry Study with Forecasts for 2015 and 2020. Freedonia Group Inc; 2011. [Accessed September 10, 2014]. Available from: http://www.freedoniagroup.com/brochure/27xx/2758smwe.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

