Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-propyl-pyridinium bromide
- PMID: 25552997
- PMCID: PMC4257424
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814025665
Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-propyl-pyridinium bromide
Abstract
The title mol-ecular salt, C8H13N2 (+)·Br(-), crystallizes with two independent 3-amino-pyridinium cations and two bromide anions in the asymmetric unit (Z' = 2). In the pyridine ring, the N atom is alkyl-ated by a propyl group. The dihedral angle between the mean planes of the pyridinium ring and the propyl group is 84.84 (2)° in cation A, whereas the corresponding angle is 89.23 (2)° in cation B. In the crystal, the anions and cations are linked via N-H⋯Br and C-H⋯Br hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along [100].
Keywords: C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds; N—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds; crystal structure; molecular salt; pyridinium salt.
Figures
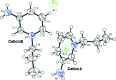
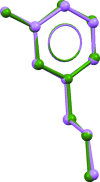
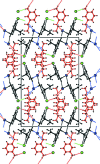
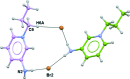
 (12) ring motif (see Table 1 ▶ for details; only the interacting atoms are labelled).
(12) ring motif (see Table 1 ▶ for details; only the interacting atoms are labelled).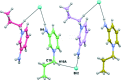
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of 4-amino-1-(4-methyl-benz-yl)pyridinium bromide.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014 Nov 26;70(Pt 12):o1293-4. doi: 10.1107/S1600536814025343. eCollection 2014 Dec 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014. PMID: 25553054 Free PMC article.
-
Bromination of bis-(pyridin-2-yl) diselenide in methyl-ene chloride: the reaction mechanism and crystal structures of 1H-pyridine-2-selenenyl dibromide and its cyclo-adduct with cyclo-pentene (3aSR,9aRS)-2,3,3a,9a-tetra-hydro-1H-cyclo-penta-[4,5][1,3]selenazolo[3,2-a]pyridinium bromide.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2019 Apr 25;75(Pt 5):675-679. doi: 10.1107/S2056989019004997. eCollection 2019 May 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2019. PMID: 31110809 Free PMC article.
-
1-Allyl-2-amino-pyridin-1-ium bromide.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013 May 15;69(Pt 6):o884. doi: 10.1107/S1600536813012452. Print 2013 Jun 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013. PMID: 23795060 Free PMC article.
-
5-Carbamoyl-2-methyl-1-(2-methyl-benz-yl)pyridinium bromide.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Jun 1;68(Pt 6):o1609-10. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812018958. Epub 2012 May 5. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22719415 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of five halido gold complexes involving piperidine or pyrrolidine as ligands or (protonated) as cations.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023 Oct 10;79(Pt 11):1017-1027. doi: 10.1107/S205698902300854X. eCollection 2023 Nov 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023. PMID: 37936840 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Experimental and Theoretical Insights into the Optical Properties and Intermolecular Interactions in Push-Pull Bromide Salts.ChemistryOpen. 2019 Apr 17;8(4):483-496. doi: 10.1002/open.201900061. eCollection 2019 Apr. ChemistryOpen. 2019. PMID: 31019874 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, intermolecular interactions and biological activities of two new organic-inorganic hybrids C6H10N2,2Br and C6H10N2,2Cl·H2O.RSC Adv. 2020 Feb 4;10(10):5864-5873. doi: 10.1039/c9ra09294c. eCollection 2020 Feb 4. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anwar, N., Kosuge, H., Okada, S., Oikawa, H. & Nakanishi, H. (2001). Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 40, 4213–4216.
-
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Calas, M., Ouattara, M., Piquet, G., Ziora, Z., Bordat, Y., Ancelin, M. L., Escale, R. & Vial, H. (2007). J. Med. Chem. 50, 6307–6315. - PubMed
-
- Ezaki, S. & Kokeguchi, N. (2006). Jpn Patent JP 2006171518.
-
- Gama, Y., Suzuki, H. & Narasaki, H. (1981). Jpn Patent JP 56139463.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
