Effect of home visit training program on growth and development of preterm infants: a double blind randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25553330
- PMCID: PMC4280552
Effect of home visit training program on growth and development of preterm infants: a double blind randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Home visit program can be effective in infants' growth and development. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of home visit program on preterm infants' growth and development within 6 months.
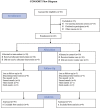
Methods: It was a double-blind clinical trial study. The study was conducted in Hafez, Hazrat-e-Zeinab, and Namazee Hospitals affiliated to Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran from 2010 to 2011. Preterm infants were divided into intervention (n=30) and control groups (n=30) through blocked randomization. The intervention group received home visit training program for 6 months, while the control group only received the hospital's routine care. Then, the infants' growth indexes, including weight, height, and head circumference, and development criteria were compared on the first day of admission in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, and then first, second, third, and sixth months. The data were analyzed using Chi-square, independent t-test, and repeated measures ANCOVA.
Results: The mean weight of the intervention and control group infants was 7207.3±1129.74 and 6366.7±922.26 gr in the sixth month. Besides, the intervention group infants' mean weight was higher compared to the control group after six months (t=-3.05, P=0.03). Also, a significant difference was found between the two groups regarding development indexes, such as following moving objects with the head, keeping the head stable when changing the position from lying to sitting, producing "Agha" sound, and taking objects by hand (P<0.05) during six months of age.
Conclusion: The results showed that the home visit program was effective in preterm infants' weight gain and some development indexes at the sixth month. Considering the importance of infants' growth and development, healthcare staff is recommended to incorporate home visit training into their programs, so that steps can be taken towards improvement of preterm infants' health.
Trial registration number: IRCT2014082013690N3
Keywords: Development; Growth; Home visit; Preterm infant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of the educational program on Iranian premature infants' parental stress in a neonatal intensive care unit: a double-blind randomized controlled trial.Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2014 Oct;2(4):240-50. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2014. PMID: 25349867 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of a parent participation improvement program for parents on partnership, attachment infant growth in a neonatal intensive care unit: A randomized controlled trial.Int J Nurs Stud. 2019 Jul;95:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.03.018. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019. PMID: 31005676 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of recorded maternal voice on anthropometric parameters and heart rate in premature infants: A pilot randomised controlled trial.J Pediatr Nurs. 2023 Sep-Oct;72:e122-e129. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2023.06.018. Epub 2023 Jun 16. J Pediatr Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37331833 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of tub bathing and sponge bathing on neonatal comfort and physiological parameters in late preterm infants: A randomized controlled trial.Int J Nurs Stud. 2019 Nov;99:103377. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.06.008. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019. PMID: 31442786 Clinical Trial.
-
Nutrition, growth, and allergic diseases among very preterm infants after hospital discharge.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4588. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461996 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Postnatal Maternal or Caregiver Interventions on Outcomes among Infants under Six Months with Growth Faltering: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 14;16(6):837. doi: 10.3390/nu16060837. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542748 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Home Visit Program Based on the Continued Kangaroo Mother Care on Maternal Resiliency and Development of Premature Infant: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2021 Jan;9(1):64-75. doi: 10.30476/ijcbnm.2020.86141.1321. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2021. PMID: 33521150 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of a guided participation discharge program for very preterm infants in a neonatal intensive care unit: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Nov 4;19(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1794-y. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31684903 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Are home visits an effective method for diabetes management? A quantitative systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes Investig. 2017 Sep;8(5):701-708. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12630. Epub 2017 Mar 11. J Diabetes Investig. 2017. PMID: 28109182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee E, Mitchell-Herzfeld SD, Lowenfels AA, et al. Reducing low birth weight through home visitation: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2009;36:154–60. - PubMed
-
- Forcada-Guex M, Pierrehumbert B, Borghini A, et al. Early dyadic patterns of mother-infant interactions and outcomes of prematurity at 18 months. Pediatrics. 2006;118:e107–14. - PubMed
-
- Wolke D, Sohne B, Riegel K, et al. An epidemiologic longitudinal study of sleeping problems and feeding experience of preterm and term children in southern Finland: comparison with a southern German population sample. The Journal of Pediatrics. 1998;133:224–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources