Etomidate-remifentanil is more suitable for monitored anesthesia care during gastroscopy in older patients than propofol-remifentanil
- PMID: 25553506
- PMCID: PMC4288392
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.891183
Etomidate-remifentanil is more suitable for monitored anesthesia care during gastroscopy in older patients than propofol-remifentanil
Abstract
Background: This prospective and randomized study was designed to compare safety, potential complications, and patient and examiner satisfaction of 2 anesthetic combinations - etomidate-remifentanil and propofol-remifentanil - in elderly patients undergoing diagnostic gastroscopy.
Material and methods: A group of 720 patients, aged 60-80 years, scheduled for diagnostic gastroscopy under sedation were prospectively randomized. After 0.4-0.6 μg kg⁻¹ of remifentanil was infused, etomidate or propofol was administered. Patients in the etomidate group received doses of etomidate at 0.1-0.15 mg kg⁻¹ followed by 4-6 mg. Patients in the propofol group received doses of propofol at 1-2 mg kg⁻¹ followed by 20-40 mg. Physiological indexes were evaluated for the 715 of 720 patients that completed the treatment. The onset time, duration time, and discharge time were recorded. Physicians, anesthetists, and patients were surveyed to assess their satisfaction.
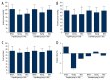
Results: Systolic pressure and diastolic pressure decreased significantly after the procedure in the propofol group (P<0.001). The average heart rate was significantly lower in the propofol group (P<0.05). No periods of desaturation (SpO₂ <95%) were observed in either group. The onset time was earlier in the etomidate group (P=0.00). All adverse events, with the exception of myoclonus, were greater in the propofol group, and physician and patient satisfaction in both groups was similar.
Conclusions: Etomidate-remifentanil administration for sedation and analgesia during gastroscopy resulted in more stable hemodynamic responses and less adverse events in older patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of etomidate-remifentanil and propofol-remifentanil sedation in patients scheduled for colonoscopy.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009 May;26(5):370-6. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328318c666. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009. PMID: 19300267 Clinical Trial.
-
Intravenous remifentanil and propofol for gastroscopy.J Clin Anesth. 2008 Aug;20(5):352-355. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2008.03.006. J Clin Anesth. 2008. PMID: 18761243 Clinical Trial.
-
Propofol and remifentanil for deep sedation in children undergoing gastrointestinal endoscopy.Paediatr Anaesth. 2007 May;17(5):460-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2006.02132.x. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007. PMID: 17474953 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of combined use of propofol and etomidate for sedation during gastroscopy: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(20):e15712. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015712. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31096522 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol decreased the etomidate-induced myoclonus in adult patients: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Feb;27(4):1322-1335. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202302_31366. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36876671
Cited by
-
Effects of small-dose remifentanil combined with index of consciousness monitoring on gastroscopic polypectomy: a prospective, randomized, single-blinded trial.Trials. 2018 Jul 18;19(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2783-4. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30021625 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Etomidate Combined with Propofol versus Remimazolam for Sedation in Elderly Patients During Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: A Randomized Prospective Clinical Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 2;18:2681-2692. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S454314. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38974124 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
ED50 and ED95 of Remimazolam Tosilate Combined with Different Doses of Fentanyl in Elderly Patients for Painless Gastroscopy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jun 18;18:2347-2356. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S462607. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38915865 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Advances in Analgosedation and Periprocedural Care for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 8;13(2):473. doi: 10.3390/life13020473. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etomidate and its Analogs: A Review of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021 Oct;60(10):1253-1269. doi: 10.1007/s40262-021-01038-6. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021. PMID: 34060021 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lucendo AJ, Arias Á, González-Castillo S, et al. Same-day bidirectional endoscopy with nonanesthesiologist administration of propofol: safety and cost-effectiveness compared with separated exams. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;26:301–8. - PubMed
-
- Falk J, Zed PJ. Etomidate for procedural sedation in the emergency department. Ann Pharmacother. 2004;38:1272–77. - PubMed
-
- Hsu WH, Wang SSW, Shih HY, et al. Low effect-site concentration of propofol target-controlled infusion reduces the risk of hypotension during endoscopy in a Taiwanese population. J Dig Dos. 2013;14:147–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical