Uncovering the novel characteristics of Asian honey bee, Apis cerana, by whole genome sequencing
- PMID: 25553907
- PMCID: PMC4326529
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-1
Uncovering the novel characteristics of Asian honey bee, Apis cerana, by whole genome sequencing
Abstract
Background: The honey bee is an important model system for increasing understanding of molecular and neural mechanisms underlying social behaviors relevant to the agricultural industry and basic science. The western honey bee, Apis mellifera, has served as a model species, and its genome sequence has been published. In contrast, the genome of the Asian honey bee, Apis cerana, has not yet been sequenced. A. cerana has been raised in Asian countries for thousands of years and has brought considerable economic benefits to the apicultural industry. A cerana has divergent biological traits compared to A. mellifera and it has played a key role in maintaining biodiversity in eastern and southern Asia. Here we report the first whole genome sequence of A. cerana.
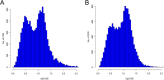
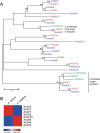
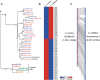
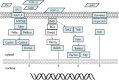
Results: Using de novo assembly methods, we produced a 238 Mbp draft of the A. cerana genome and generated 10,651 genes. A.cerana-specific genes were analyzed to better understand the novel characteristics of this honey bee species. Seventy-two percent of the A. cerana-specific genes had more than one GO term, and 1,696 enzymes were categorized into 125 pathways. Genes involved in chemoreception and immunity were carefully identified and compared to those from other sequenced insect models. These included 10 gustatory receptors, 119 odorant receptors, 10 ionotropic receptors, and 160 immune-related genes.
Conclusions: This first report of the whole genome sequence of A. cerana provides resources for comparative sociogenomics, especially in the field of social insect communication. These important tools will contribute to a better understanding of the complex behaviors and natural biology of the Asian honey bee and to anticipate its future evolutionary trajectory.
Figures


References
-
- Galizia CG, Eisenhardt D, Giurfa M, Menzel R. Honeybee Neurobiology and Behavior : A Tribute to Randolf Menzel. Dordrecht Netherlands. New York: Springer; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

