MiRNA inhibition in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
- PMID: 25553957
- PMCID: PMC4485980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.12.006
MiRNA inhibition in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
Abstract
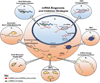
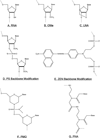
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are noncoding RNAs that provide an endogenous negative feedback mechanism for translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) into protein. Single miRNAs can regulate hundreds of mRNAs, enabling miRNAs to orchestrate robust biological responses by simultaneously impacting multiple gene networks. MiRNAs can act as master regulators of normal and pathological tissue development, homeostasis, and repair, which has motivated expanding efforts toward the development of technologies for therapeutically modulating miRNA activity for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering applications. This review highlights the tools currently available for miRNA inhibition and their recent therapeutic applications for improving tissue repair.
Keywords: Anti-miR; MiRNA; MiRNA inhibition; Regenerative medicine; Tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Weiler J, Hunziker J, Hall J. Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides (AMOs): ammunition to target miRNAs implicated in human disease? Gene therapy. 2005;13(6):496–502. - PubMed
-
- Coelho T, Adams D, Silva A, Lozeron P, Hawkins PN, Mant T, Perez J, Chiesa J, Warrington S, Tranter E, Munisamy M, Falzone R, Harrop J, Cehelsky J, Bettencourt BR, Geissler M, Butler JS, Sehgal A, Meyers RE, Chen Q, Borland T, Hutabarat RM, Clausen VA, Alvarez R, Fitzgerald K, Gamba-Vitalo C, Nochur SV, Vaishnaw AK, Sah DW, Gollob JA, Suhr OB. Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(9):819–829. - PubMed
-
- Graham MJ, Lee RG, Bell TA, 3rd, Fu W, Mullick AE, Alexander VJ, Singleton W, Viney N, Geary R, Su J, Baker BF, Burkey J, Crooke ST, Crooke RM. Antisense oligonucleotide inhibition of apolipoprotein C-III reduces plasma triglycerides in rodents, nonhuman primates, and humans. Circ Res. 2013;112(11):1479–1490. - PubMed
-
- Tanioka M, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Yamada Y, Yamada K, Goto Y, Fujimoto T, Sekiguchi R, Uenaka K, Callies S, Tamura T. Phase I study of LY2181308, an antisense oligonucleotide against survivin, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;68(2):505–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

