Abnormal expression of serum soluble E-cadherin is correlated with clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer
- PMID: 25553984
- PMCID: PMC4280058
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.892049
Abnormal expression of serum soluble E-cadherin is correlated with clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Increased amounts of soluble E-cadherin (E-cad) have been found in the serum in various cancers, but the role of serum soluble E-cad in the prognosis of breast cancer patients has not been explored in Asian populations.
Material/method: Blood samples from 111 consecutive patients diagnosed with breast cancer and 55 healthy controls were investigated.Serum soluble E-cad expression levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA) with an immunoassay kit according to the manufacturer's directions. Kaplan-Meier analyses were used to evaluate the association between serum soluble E-cad expression level and survival. All statistical tests were 2-sided.
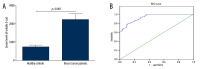
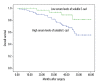
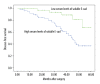
Results: The serum levels of soluble E-cad in breast cancer patients were significantly higher than those of the control group (2218.9±319.6 ng/ml vs. 742.8±91.7 ng/ml, p<0.001). Serum levels of soluble E-cad correlated significantly with TNM stage (P=0.007), tumor grade (P=0.03), and lymph node metastasis (P<0.001). Kaplan-Meier analysis with the log-rank test indicated that high serum levels of soluble E-cad had a significant impact on overall survival (55.4% vs. 81.4%; P=0.032) and disease-free survival (36.8% vs. 67.8%; P=0.002) in breast cancer. Multivariate analysis revealed that serum levels of soluble E-cad were independently associated with overall survival and disease-free survival in breast cancer patients.
Conclusions: Serum soluble E-cad level is an independent prognostic factor in Asian breast cancer patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined expression of ezrin and E-cadherin is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in breast cancer.Oncol Rep. 2015 Jul;34(1):165-74. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3967. Epub 2015 May 8. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25955302
-
Significance of the serum level of soluble E-cadherin in patients with HCC.Hepatogastroenterology. 2008 Jul-Aug;55(85):1390-3. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18795696
-
The predictive value of serum soluble E-cadherin levels in breast cancer patients undergoing preoperative systemic chemotherapy.Clin Biochem. 2013 Oct;46(15):1585-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Clin Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23792261
-
Diagnostic and prognostic potential of serum angiopoietin-2 expression in human breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jan 1;8(1):660-4. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25755760 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of soluble E-cadherin in breast, gastric, and colorectal cancers.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:408047. doi: 10.1155/2014/408047. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25535613 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cadherin Signaling in Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 12;22(24):13358. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413358. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Sensor for Cancer Biomarker Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;13(3):396. doi: 10.3390/bios13030396. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-506 Over-Expression Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jun 10;21:1687-92. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893522. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26059632 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression of CDH1 or CTNNB1 affects poor prognosis of patients with esophageal cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Sep 6;14(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0956-8. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27600761 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Level of Genes Coding for Cell Adhesion Molecules of Cadherin Group in Colorectal Cancer Patients.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jul 13;21:2031-40. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893610. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26167814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Li LP, Lu CH, Chen ZP, et al. Subcellular proteomics revealed the epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in lung cancer. Proteomics. 2011;11:429–39. - PubMed
-
- Soltermann A, Tischler V, Arbogast S, et al. Prognostic significance of epithelial-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-epithelial transition protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:7430–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

