Induced neural stem cells protect neuronal cells against apoptosis
- PMID: 25554259
- PMCID: PMC4280057
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.891343
Induced neural stem cells protect neuronal cells against apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Neuronal cells are vulnerable to many stresses that can cause apoptosis. Reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced neural stem cells (iNSCs) is a potentially unlimited source of neurons. Discovering agents that can provide neuronal protection against these apoptotic stimuli is important for developing therapeutic strategies for various brain diseases.
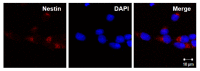
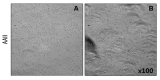
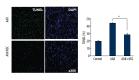
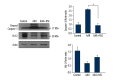
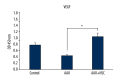
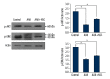
Material and methods: We investigated the therapeutic effects of iNSCs against apoptosis activator II (AAII)-induced apoptosis of cortical neuronal cells. Apoptosis was confirmed by double immunocytochemistry with NeuN and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated digoxigenin-dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling. We performed Western blot analyses for activated caspase-3, Bcl-2, phosphorylated Akt, and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK). The level of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was analyzed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (P<0.05).
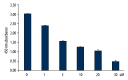
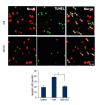
Results: Cortical neuronal cells cultured with iNSCs had fewer apoptotic cells than those cultured without iNSCs. We found that cells cultured with iNSCs had a significantly lower caspase-3 level and a significantly higher Bcl-2 level than cells cultured without iNSCs. Cells cultured with iNSCs had higher VEGF levels than cells cultured without iNSCs. The levels of phosphorylated Akt and phosphorylated ERK were significantly higher in cells cultured with iNSCs than in cells cultured without iNSCs.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that iNSCs activate Akt and ERK, which are associated with the inhibition of neuronal apoptosis. Thus, treatment with iNSCs may help reduce neuronal loss in brain disease. Further studies aimed at proving this hypothesis might help establish therapeutic agents that can prevent neuronal cell death and help cure neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Reynoids BA, Welss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255:1707–10. - PubMed
-
- Han DW, Tapia N, Hermann A, et al. Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into neural stem cells by defined factors. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;6:465–72. - PubMed
-
- Guo F, Lv S, Lou Y, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells enhance the angiogenesis in ischaemic cortex after stroke: involvement of notch signalling. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36:997–1004. - PubMed
-
- Hicks AU, Lappalainen RS, Narkilahti S, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cellderived neural precursor cells and enriched environment after cortical stroke in rats: cell survival and functional recovery. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;29:562–74. - PubMed
-
- Burg ED, Remillard CV, Yuan JX. K+ channels in apoptosis. J Membr Biol. 2006;209(1):3–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

