Mosquito genomics. Highly evolvable malaria vectors: the genomes of 16 Anopheles mosquitoes
- PMID: 25554792
- PMCID: PMC4380271
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1258522
Mosquito genomics. Highly evolvable malaria vectors: the genomes of 16 Anopheles mosquitoes
Abstract
Variation in vectorial capacity for human malaria among Anopheles mosquito species is determined by many factors, including behavior, immunity, and life history. To investigate the genomic basis of vectorial capacity and explore new avenues for vector control, we sequenced the genomes of 16 anopheline mosquito species from diverse locations spanning ~100 million years of evolution. Comparative analyses show faster rates of gene gain and loss, elevated gene shuffling on the X chromosome, and more intron losses, relative to Drosophila. Some determinants of vectorial capacity, such as chemosensory genes, do not show elevated turnover but instead diversify through protein-sequence changes. This dynamism of anopheline genes and genomes may contribute to their flexible capacity to take advantage of new ecological niches, including adapting to humans as primary hosts.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
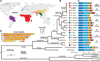
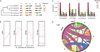



Comment in
-
Evolutionary genomics. Conundrum of jumbled mosquito genomes.Science. 2015 Jan 2;347(6217):27-8. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa3600. Science. 2015. PMID: 25554775 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cohuet A, Harris C, Robert V, Fontenille D. Evolutionary forces on Anopheles: what makes a malaria vector? Trends Parasitol. 2010;26:130–136. - PubMed
-
- Manguin S, C P, Mouchet J, E JL. Biodiversity of Malaria in the World. John Libbey Eurotext; 2008.
-
- Holt RA. The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science. 2002;298:129–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 AI080799/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G1100339/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R21 AI101459/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG007234/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063508/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI089686/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI110818/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104956/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050243/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM080178/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095842/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- SC1 AI109055/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI107263/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076584/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 092654/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

