Intra-session test-retest reliability of magnitude and structure of center of pressure from the Nintendo Wii Balance Board™ for a visually impaired and normally sighted population
- PMID: 25555361
- PMCID: PMC4385439
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2014.11.012
Intra-session test-retest reliability of magnitude and structure of center of pressure from the Nintendo Wii Balance Board™ for a visually impaired and normally sighted population
Abstract
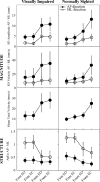
Individuals with visual impairment (VI) have irreparable damage to one of the input streams contributing to postural stability. Here, we evaluated the intra-session test-retest reliability of the Wii Balance Board (WBB) for measuring Center of Pressure (COP) magnitude and structure, i.e. approximate entropy (ApEn) in fourteen legally blind participants and 21 participants with corrected-to-normal vision. Participants completed a validated balance protocol which included four sensory conditions: double-leg standing on a firm surface with eyes open (EO-firm); a firm surface with eyes closed (EC-firm); a foam surface with EO (EO-foam); and a foam surface with EC (EC-foam). Participants performed the full balance protocol twice during the session, separated by a period of 15min, to determine the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Absolute reliability was determined by the standard error of measurement (SEM). The minimal difference (MD) was estimated to determine clinical significance for future studies. COP measures were derived from data sent by the WBB to a laptop via Bluetooth. COP scores increased with the difficulty of sensory condition indicating WBB sensitivity (all p<0.01). ICCs in the VI group ranged from 0.73 to 0.95, indicating high to very high correlations, and the normal group showed moderate to very high ICCs (0.62-0.94). The SEM was comparable between groups regardless of between-subject variability. The reliability of the WBB makes it practical to screen for balance impairment among VI persons.
Keywords: Approximate entropy; Center of pressure; Reliability; Vision impairment; Wii Balance Board.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Yim-Chiplis PK, Talbot LA. Defining and measuring balance in adults. Biological Research for Nursing. 2000;1:321–31. - PubMed
-
- Elliott DB, Patla AE, Flanagan J, Spaulding S, Rietdyk S, Strong G, et al. The Waterloo Vision and Mobility Study – Postural Control Strategies in Subjects with Arm. Ophthal Physl Opt. 1995;15:553–9. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson GP, Newman CW, Kartush JM. Handbook of balance function testing. Singular Pub Group. 1997
-
- Odom J, Odom C, Leys M. Does Improving Vision Reduce the Risk of Falls? A Review. Insight: Research and Practice in Visual Impairment and Blindness. 2011;4:92–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials