Review: Modulating the unfolded protein response to prevent neurodegeneration and enhance memory
- PMID: 25556298
- PMCID: PMC5053297
- DOI: 10.1111/nan.12211
Review: Modulating the unfolded protein response to prevent neurodegeneration and enhance memory
Abstract
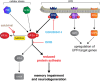
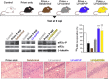
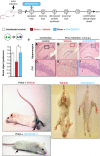
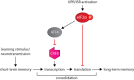
Recent evidence has placed the unfolded protein response (UPR) at the centre of pathological processes leading to neurodegenerative disease. The translational repression caused by UPR activation starves neurons of the essential proteins they need to function and survive. Restoration of protein synthesis, via genetic or pharmacological means, is neuroprotective in animal models, prolonging survival. This is of great interest due to the observation of UPR activation in the post mortem brains of patients with Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, tauopathies and prion diseases. Protein synthesis is also an essential step in the formation of new memories. Restoring translation in disease or increasing protein synthesis from basal levels has been shown to improve memory in numerous models. As neurodegenerative diseases often present with memory impairments, targeting the UPR to both provide neuroprotection and enhance memory provides an extremely exciting novel therapeutic target.
Keywords: memory; neurodegeneration; neurodegenerative diseases; therapeutics; unfolded protein response.
© 2014 The Authors. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Neuropathological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Haass C, Selkoe DJ. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer's amyloid beta‐peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 101–112 - PubMed
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau‐mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007; 8: 663–672 - PubMed
-
- Breydo L, Wu JW, Uversky VN. Alpha‐synuclein misfolding and Parkinson's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012; 1822: 261–285 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

