Low affinity binding site clusters confer hox specificity and regulatory robustness
- PMID: 25557079
- PMCID: PMC4449256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.041
Low affinity binding site clusters confer hox specificity and regulatory robustness
Abstract
In animals, Hox transcription factors define regional identity in distinct anatomical domains. How Hox genes encode this specificity is a paradox, because different Hox proteins bind with high affinity in vitro to similar DNA sequences. Here, we demonstrate that the Hox protein Ultrabithorax (Ubx) in complex with its cofactor Extradenticle (Exd) bound specifically to clusters of very low affinity sites in enhancers of the shavenbaby gene of Drosophila. These low affinity sites conferred specificity for Ubx binding in vivo, but multiple clustered sites were required for robust expression when embryos developed in variable environments. Although most individual Ubx binding sites are not evolutionarily conserved, the overall enhancer architecture-clusters of low affinity binding sites-is maintained and required for enhancer function. Natural selection therefore works at the level of the enhancer, requiring a particular density of low affinity Ubx sites to confer both specific and robust expression.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
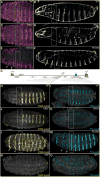
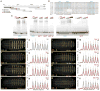

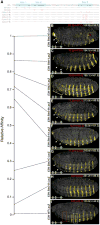
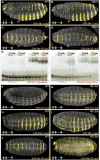

Comment in
-
Toward a new twist in Hox and TALE DNA-binding specificity.Dev Cell. 2015 Feb 9;32(3):259-61. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.01.030. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25669880
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

