Visually induced nausea causes characteristic changes in cerebral, autonomic and endocrine function in humans
- PMID: 25557265
- PMCID: PMC4358679
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.284240
Visually induced nausea causes characteristic changes in cerebral, autonomic and endocrine function in humans
Abstract
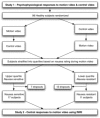
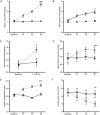
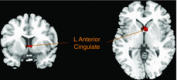
An integrated understanding of the physiological mechanisms involved in the genesis of nausea remains lacking. We aimed to describe the psychophysiological changes accompanying visually induced motion sickness, using a motion video, hypothesizing that differences would be evident between subjects who developed nausea in comparison to those who did not. A motion, or a control, stimulus was presented to 98 healthy subjects in a randomized crossover design. Validated questionnaires and a visual analogue scale (VAS) were used for the assessment of anxiety and nausea. Autonomic and electrogastrographic activity were measured at baseline and continuously thereafter. Plasma vasopressin and ghrelin were measured in response to the motion video. Subjects were stratified into quartiles based on VAS nausea scores, with the upper and lower quartiles considered to be nausea sensitive and resistant, respectively. Twenty-eight subjects were exposed to the motion video during functional neuroimaging. During the motion video, nausea-sensitive subjects had lower normogastria/tachygastria ratio and cardiac vagal tone but higher cardiac sympathetic index in comparison to the control video. Furthermore, nausea-sensitive subjects had decreased plasma ghrelin and demonstrated increased activity of the left anterior cingulate cortex. Nausea VAS scores correlated positively with plasma vasopressin and left inferior frontal and middle occipital gyri activity and correlated negatively with plasma ghrelin and brain activity in the right cerebellar tonsil, declive, culmen, lingual gyrus and cuneus. This study demonstrates that the subjective sensation of nausea is associated with objective changes in autonomic, endocrine and brain networks, and thus identifies potential objective biomarkers and targets for therapeutic interventions.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2015 The Physiological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional brain networks and neuroanatomy underpinning nausea severity can predict nausea susceptibility using machine learning.J Physiol. 2019 Mar;597(6):1517-1529. doi: 10.1113/JP277474. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30629751 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in autonomic responses between subjects with and without nausea while watching an irregularly oscillating video.Auton Neurosci. 2004 Nov 30;116(1-2):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2004.08.008. Auton Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15556837
-
Vasopressin and oxytocin responses to illusory self-motion and nausea in man.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Nov;71(5):1269-75. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-5-1269. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990. PMID: 2229284
-
Illusory self-motion and motion sickness: a model for brain-gut interactions and nausea.Dig Dis Sci. 1999 Aug;44(8 Suppl):53S-57S. Dig Dis Sci. 1999. PMID: 10490040 Review.
-
Motion and space sickness: intestinal and autonomic correlates.Auton Neurosci. 2006 Oct 30;129(1-2):58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2006.07.020. Epub 2006 Sep 6. Auton Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16950658 Review.
Cited by
-
A History of Drug Discovery for Treatment of Nausea and Vomiting and the Implications for Future Research.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 4;9:913. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00913. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30233361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resting Heart Rate Variability (HRV) in Adolescents and Young Adults from a Genetically-Informed Perspective.Behav Genet. 2018 Sep;48(5):386-396. doi: 10.1007/s10519-018-9915-1. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Behav Genet. 2018. PMID: 29995284 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Visually Induced Motion Sickness: An eLORETA Study.Brain Topogr. 2024 Nov 2;38(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s10548-024-01088-6. Brain Topogr. 2024. PMID: 39487878 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ghrelin and motilin receptors as drug targets for gastrointestinal disorders.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jan;13(1):38-48. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.163. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26392067 Review.
-
Prior transfusion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can effectively alleviate symptoms of motion sickness in mice through interleukin 10 secretion.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Feb 26;13(2):177-192. doi: 10.4252/wjSC.v13.i2.177. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33708346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews PL. Sanger GJ. Nausea and the quest for the perfect anti-emetic. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;722:108–121. - PubMed
-
- Benarroch EE, Opfer-Gehrking TL. Low PA. Use of the photoplethysmographic technique to analyze the Valsalva maneuver in normal man. Muscle Nerve. 1991;14:1165–1172. - PubMed
-
- Benson PW, Hooker JB, Koch KL. Weinberg RB. Bitter taster status predicts susceptibility to vection-induced motion sickness and nausea. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;24:134–140. e186. - PubMed
-
- Bos JE. Bles W. Motion sickness induced by optokinetic drums. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2004;75:172–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

