A Simple Capacitive Charge-Division Readout for Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Arrays
- PMID: 25558081
- PMCID: PMC4281963
- DOI: 10.1109/TNS.2013.2275012
A Simple Capacitive Charge-Division Readout for Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Arrays
Abstract
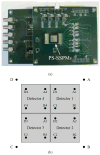
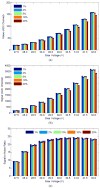
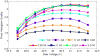
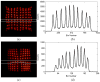
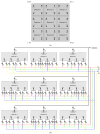
A capacitive charge-division readout method for reading out a 2 × 2 array of 5 mm × 5 mm position-sensitive solid-state photomultipliers (PS-SSPM) was designed and evaluated. Using this analog multiplexing method, the 20 signals (16 position, 4 timing) from the PS-SSPM array are reduced to 5 signals (4 position, 1 timing), allowing the PS-SSPM array to be treated as an individual large-area PS-SSPM module. A global positioning approach can now be used, instead of individual positioning for each PS-SSPM in the array, ensuring that the entire light signal is utilized. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and flood histogram quality at different bias voltages (27.5 V to 32.0 V at 0.5 V intervals) and a fixed temperature of 0 °C were evaluated by coupling a 6 × 6 array of 1.3 mm × 1.3 mm × 20 mm polished LSO crystals to the center of the PS-SSPM array. The timing resolution was measured at a fixed bias voltage of 31.0 V and a fixed temperature of 0 °C. All the measurements were evaluated and compared using capacitors with different values and tolerances. Capacitor values ranged from 0.051 nf to 10 nf, and the capacitance tolerance ranged from 1% to 20%. The results show that better performance was achieved using capacitors with smaller values and better capacitance tolerance. Using 0.2 nf capacitors, the SNR, energy resolution and timing resolution were 24.3, 18.2% and 8.8 ns at a bias voltage 31.0 V, respectively. The flood histogram quality was also evaluated by using a 10 × 10 array of 1 mm × 1 mm × 10 mm polished LSO crystals and a 10 × 10 array of 0.7 mm × 0.7 mm × 20 mm unpolished LSO crystals to determine the smallest crystal size resolvable. These studies showed that the high spatial resolution of the PS-SSPM was preserved allowing for 0.7 mm crystals to be identified. These results show that the capacitive charge-division analog signal processing method can significantly reduce the number of electronic channels, from 20 to 5, while retaining the excellent performance of the detector.
Keywords: Capacitive Charge–Division Readout; Electronics; PET; PS-SSPM.
Figures





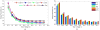



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Matrix9 silicon photomultiplier array for small-animal PET.Med Phys. 2015 Feb;42(2):585. doi: 10.1118/1.4905088. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 25652479 Free PMC article.
-
Performance Comparison of Different Readouts for Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Arrays.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2017 Aug;3(4):045019. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/aa7c6a. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2017. PMID: 29915669 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of large-area position-sensitive solid-state photomultipliers for small animal PET.Phys Med Biol. 2012 Dec 21;57(24):8119-34. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/24/8119. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Phys Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23172720
-
A Study of Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Signal Properties.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2014 Jun 12;61(3):1074-1083. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2014.2302635. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2014. PMID: 25473125 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging and Timing Performance of 1cm × 1cm Position-sensitive Solid-state Photomultiplier.J Instrum. 2013 Feb;8(2):C02033. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/8/02/C02033. J Instrum. 2013. PMID: 25540669 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Thermal regulation of tightly packed solid-state photodetectors in a 1 mm(3) resolution clinical PET system.Med Phys. 2015 Jan;42(1):305-13. doi: 10.1118/1.4903889. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 25563270 Free PMC article.
-
Technical opportunities and challenges in developing total-body PET scanners for mice and rats.EJNMMI Phys. 2023 Jan 2;10(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40658-022-00523-6. EJNMMI Phys. 2023. PMID: 36592266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High spatial resolution PET detectors based on 10 mm × 10 mm linearly-graded SiPMs and 0.5 mm pitch LYSO arrays.Phys Med Biol. 2025 Jan 17;70(2):10.1088/1361-6560/ada084. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ada084. Phys Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39689427
-
Evaluation of Matrix9 silicon photomultiplier array for small-animal PET.Med Phys. 2015 Feb;42(2):585. doi: 10.1118/1.4905088. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 25652479 Free PMC article.
-
Performance Comparison of Different Readouts for Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Arrays.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2017 Aug;3(4):045019. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/aa7c6a. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2017. PMID: 29915669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McClish M, Dokhale P, Christian J, Stapels C, Johnson E, Robertson R, Shah KS. Performance measurements of CMOS position sensitive solid-state photomultipliers. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2010 Aug;57(4):2280–2286.
-
- Lewellen T. The challenge of detector designs for PET. Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2010 Aug;195(2):301–309. - PubMed
-
- Schmall J, Du J, Yang Y, Dokhale P, McClish M, Shah K, Cherry SR. Comparison of large-area position-sensitive solid-state photomultipliers for small animal PET. Phys Med Biol. 2012 Dec;57(24):8119–8134. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
