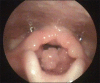
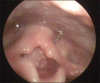
Anesthesia management in a child with laryngeal papilloma causing near complete airway obstruction
- PMID: 25558205
- PMCID: PMC4279356
- DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.146322
Anesthesia management in a child with laryngeal papilloma causing near complete airway obstruction
Abstract
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is a rare, chronic disease of viral etiology affecting most commonly larynx. A 5-year-old child with stridor was posted for microlaryngoscopic excision of laryngeal papilloma. We discuss the perioperative management of case with the various ventilation strategies. In child with stridor intubation remains the safest option. It is suggested to maintain spontaneous ventilation until intubation as mask ventilation could be difficult.
Keywords: Anesthesia; laryngeal papilloma; stridor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Andrus JG, Shapshay SM. Contemporary management of laryngeal papilloma in adults and children. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006;39:135–58. - PubMed
-
- Derkay CS, Wiatrak B. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A review. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:1236–47. - PubMed
-
- Bo L, Wang B, Shu SY. Anesthesia management in pediatric patients with laryngeal papillomatosis undergoing suspension laryngoscopic surgery and a review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;75:1442–5. - PubMed
-
- Crastnopol P, Platt N, Phillips WR, Mesbah M, Henry EI, Aaron RS. Resection of solitary tracheal papilloma using cardiopulmonary bypass. N Y State J Med. 1967;67:1166–9. - PubMed
-
- Cohen SR, Geller KA, Seltzer S, Thompson JW. Papilloma of the larynx and tracheobronchial tree in children. A retrospective study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1980;89:497–503. - PubMed