Neuroprotective effects of the immunomodulatory drug Setarud on cerebral ischemia in male rats
- PMID: 25558220
- PMCID: PMC4281408
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.27.001
Neuroprotective effects of the immunomodulatory drug Setarud on cerebral ischemia in male rats
Abstract
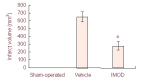
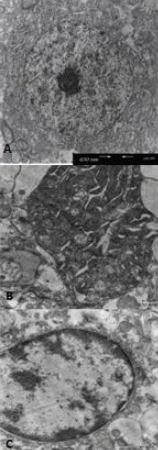
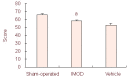
Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant agents can alleviate ischemic cerebral injury. The immunomodulary drug Setarud, which is composed of herbal extracts including Rosa canina, Urtica dioica and Tanacetum vulgare, supplemented with selenium exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. Therefore, we hypothesized that Setarud will have a neuroprotective effect against ischemic cerebral injury. To validate this hypothesis, rats were intraperitoneally administered with 0.66 mL/kg Setarud for 30 minutes after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining showed that Setarud could reduce cerebral infarct volume of rats subjected to cerebral ischemia. Transmission electron microscopy and hematoxylin-eosin staining results showed that Setarud could alleviate the degenerative changes in cortical neurons of rats with cerebral ischemia. The inclined plate test and prehensile test showed that Setarud could significantly improve the motor function of rats with cerebral ischemia. These findings suggest that Setarud shows neuroprotective effects against ischemic brain injury.
Keywords: antioxidant; brain injury; cerebral infarct; cortex; immunomodulatory drug; inclined plate test; neural regeneration; neuroprotection; prehensile test; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effects of setarud against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2008 May-Jun;27(3):110-2. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18787281
-
Safety and efficacy of Setarud (IMOD TM ) among people living with HIV/AIDS: a review.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2012 Apr;7(1):66-72. doi: 10.2174/157489112799829756. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22353002 Review.
-
Neuroprotective effect of baicalin on focal cerebral ischemia in rats.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Dec;13(12):2129-2133. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.241464. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30323141 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of daidzein on focal cerebral ischemia injury in rats.Neural Regen Res. 2015 Jan;10(1):146-52. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.150724. Neural Regen Res. 2015. PMID: 25788936 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of minocycline on focal cerebral ischemia injury: a systematic review.Neural Regen Res. 2020 May;15(5):773-782. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.268898. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31719236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nepeta Dschuparensis Bornm Extract Moderates COX-2 and IL-1β Proteins in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia.Iran J Med Sci. 2017 Mar;42(2):179-186. Iran J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28360444 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Type 1 (FGF1)-Overexpressed Adipose-Derived Mesenchaymal Stem Cells (AD-MSCFGF1) Induce Neuroprotection and Functional Recovery in a Rat Stroke Model.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017 Oct;13(5):670-685. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9755-z. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017. PMID: 28795363
-
Effect of IMOD™ on the inflammatory process after acute ischemic stroke: a randomized clinical trial.Daru. 2013 Mar 20;21(1):26. doi: 10.1186/2008-2231-21-26. Daru. 2013. PMID: 23514014 Free PMC article.
-
Tetramethylpyrazine Ameliorates Rotenone-Induced Parkinson's Disease in Rats: Involvement of Its Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Actions.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Sep;54(7):4866-4878. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0028-7. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27514753
-
The effect of Rosa canina L. and a polyherbal formulation syrup in patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 May 23;23(1):434. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06297-7. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35606864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khairandish P, Mohraz M, Farzamfar B, et al. Preclinical and phase 1 clinical safety of Setarud (IMOD™), a novel immunomodulator. DARU. 2009;17(3):148–156.
-
- Khorram-Khorshid HR, Abdollahi M, Novitsky YA, et al. Studies on potential mutagenic and genotoxic activity of Setarud. DARU. 2008;16(4):223–228.
-
- Baghaei A, Esmaily H, Bdolghaffari AH, et al. Efficacy of Setarud (IMOD), a novel drug with potent anti-toxic stress potential in rat inflammatory bowel disease and comparison with dexamethasone and infliximab. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2010;47:219–226. - PubMed
-
- Khorram-Khorshid HR, Azonov JA, Novitsky YA, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of setarud against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2008;27:110–112. - PubMed
-
- Khorram-Khorshid HR, Azonov JA, Novitsky YA, et al. Protective effects of setarud (IMODTM) on development of diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rabbits. DARU. 2008;16(4):218–222.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
