Salutary effect of pre-treatment with an Nrf2 inducer on ischemia reperfusion injury in the rat liver
- PMID: 25558293
- PMCID: PMC4280567
- DOI: 10.3968/5206
Salutary effect of pre-treatment with an Nrf2 inducer on ischemia reperfusion injury in the rat liver
Abstract
Background: Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a common phenomenon occurring during liver surgery, transplantation, and trauma. IRI causes oxidative stress which plays a critical role in causing organ damage. The Nrf2 is the master regulator of numerous genes, encoding antioxidant, detoxifying, and cytoprotective molecules. Nrf2 dysfunction has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory disorders, cancer, and aging. This study was undertaken to investigate the effect of Nrf2 pathway activator (dh404) on warm liver IRI in a rodent model.
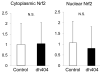
Methods: Ten Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with dh404 or vehicle. Dh404 was dissolved in sesame oil and was given orally (1.5mg/kg) the night before and 5 hours before procedures. Rat livers were subjected to 60 minutes of 70% ischemia followed by 3 hours of reperfusion. Serum ALT and Malondialdehyde (MDA) were determined and liver tissue was processed for histological examination, and determination of apoptosis, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, ADP/ATP ratio, and expressions of Nrf2, eNOS, anti-oxidant enzymes, and inflammatory mediators.
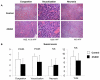
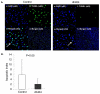
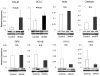
Results: Serum ALT and MDA levels and tissue MPO activity were significantly lower, expression of the anti-oxidant enzyme, glutamate cysteine ligase were significantly higher, whereas expression of NFkB and COX-2 was unchanged in the dh404-treated group. Although the total Suzuki histology score did not differ significantly, the extent of sinusoidal congestion, vacuolization, and apoptosis was significantly reduced in the dh404 treated compared to the untreated group (P<0.01).
Conclusions: Pre-treatment with dh404 resulted in partial attenuation of hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats.
Keywords: Reactive Oxygen Species; bardoxolone methyl analogue; inflammation; ischemia reperfusion injury; liver; oxidative stress.
Figures
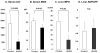
Similar articles
-
Treatment with dimethyl fumarate ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jul 7;23(25):4508-4516. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28740339 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Nrf2 pathway activation on human pancreatic islet cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 25;10(6):e0131012. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131012. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26110640 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) activator dh404 protects against diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Mar 3;16(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0513-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28253885 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent deleterious and salutary actions of the Nrf2 inducer dh404 in chronic kidney disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Sep;86:374-81. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25930007
-
Overactivation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2-antioxidant response element pathway in hepatocytes decreases hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.Liver Transpl. 2016 Jan;22(1):91-102. doi: 10.1002/lt.24303. Liver Transpl. 2016. PMID: 26285140 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hepatocyte-Specific Deficiency of BAP31 Amplified Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Attenuating Nrf2 Signaling Activation in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 5;22(19):10788. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910788. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639126 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of gastrodin pretreatment on mouse hepatic ischemia-reperfusion occurring through antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms.Exp Ther Med. 2021 May;21(5):471. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9902. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33767766 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin-carrying nanoparticles prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury in human renal cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):87390-87401. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13626. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27901497 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with dimethyl fumarate ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jul 7;23(25):4508-4516. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28740339 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin Attenuates Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Upregulation of Nrf2 through Akt/GSK3β Signaling.Molecules. 2018 Dec 29;24(1):110. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010110. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30597971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baskin-Bey ES, Washburn K, Feng S, Oltersdorf T, Shapiro D, Huyghe M, et al. Clinical Trial of the Pan-Caspase Inhibitor, IDN-6556, in Human Liver Preservation Injury. Am J Transplant. 2007;7(1):218–25. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Kan Q, Li J, Zhang X, Qi Y. Effect of neferine on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(7):2536–9. - PubMed
-
- Busuttil R. Liver ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Br J Surg. 2007;94(7):787–8. - PubMed
-
- Andrews NC, Erdjument-Bromage H, Davidson MB, Tempst P, Orkin SH. Erythroid transcription factor NF-E2 is a haematopoietic-specific basic-leucine zipper protein. Nature. 1993;362(6422):722–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
