Sex-based differences in skeletal muscle kinetics and fiber-type composition
- PMID: 25559153
- PMCID: PMC4285578
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00024.2014
Sex-based differences in skeletal muscle kinetics and fiber-type composition
Abstract
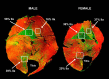
Previous studies have identified over 3,000 genes that are differentially expressed in male and female skeletal muscle. Here, we review the sex-based differences in skeletal muscle fiber composition, myosin heavy chain expression, contractile function, and the regulation of these physiological differences by thyroid hormone, estrogen, and testosterone. The findings presented lay the basis for the continued work needed to fully understand the skeletal muscle differences between males and females.
©2015 Int. Union Physiol. Sci./Am. Physiol. Soc.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Altuwaijri S, Lee DK, Chuang KH, Ting HJ, Yang Z, Xu Q, Tsai MY, Yeh S, Hanchett LA, Chang HC, Chang C. Androgen receptor regulates expression of skeletal muscle-specific proteins and muscle cell types. Endocrine 25: 27–32, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Amelink GJ, Bar PR. Exercise-induced muscle protein leakage in the rat. Effects of hormonal manipulation. J Neurol Sci 76: 61–68, 1986. - PubMed
-
- Amelink GJ, Koot RW, Erich WB, Van Gijn J, Bar PR. Sex-linked variation in creatine kinase release, and its dependence on oestradiol, can be demonstrated in an in-vitro rat skeletal muscle preparation. Acta Physiol Scand 138: 115–124, 1990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

