High-density mapping of the MHC identifies a shared role for HLA-DRB1*01:03 in inflammatory bowel diseases and heterozygous advantage in ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 25559196
- PMCID: PMC4310771
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3176
High-density mapping of the MHC identifies a shared role for HLA-DRB1*01:03 in inflammatory bowel diseases and heterozygous advantage in ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Genome-wide association studies of the related chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) known as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis have shown strong evidence of association to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). This region encodes a large number of immunological candidates, including the antigen-presenting classical human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules. Studies in IBD have indicated that multiple independent associations exist at HLA and non-HLA genes, but they have lacked the statistical power to define the architecture of association and causal alleles. To address this, we performed high-density SNP typing of the MHC in >32,000 individuals with IBD, implicating multiple HLA alleles, with a primary role for HLA-DRB1*01:03 in both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Noteworthy differences were observed between these diseases, including a predominant role for class II HLA variants and heterozygous advantage observed in ulcerative colitis, suggesting an important role of the adaptive immune response in the colonic environment in the pathogenesis of IBD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
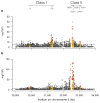


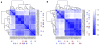

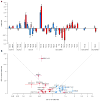
References
-
- Horton R, et al. Gene map of the extended human MHC. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:889–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA141743/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DE023789/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DE023789-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- C0482/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062432/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064869/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HS021747/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- U01 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ETM/75/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- 102974/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/540/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- ETM/137/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062429-14/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0800675/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS049477/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HS021747/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- U01 DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI067068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK046763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK046763-19/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- WT098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0600329/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U19 AI067152/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NIHR-RP-R3-12-026/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- CA141743/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

