The effects of oxytocin on cognitive defect caused by chronic restraint stress applied to adolescent rats and on hippocampal VEGF and BDNF levels
- PMID: 25559382
- PMCID: PMC4294596
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.893159
The effects of oxytocin on cognitive defect caused by chronic restraint stress applied to adolescent rats and on hippocampal VEGF and BDNF levels
Abstract
Background: Because brain development continues during adolescence, the effects of chronic stress on hippocampal changes that occur during that period are permanent. Oxytocin, which is synthesized in the hypothalamus and has many receptors in brain regions, including the hippocampus, may affect learning-memory. This study aimed to investigate chronic restraint stress on hippocampal functions, and hippocampal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in adolescent male and female rats and the role of oxytocin in these effects.
Material/methods: Experimental groups included control, stress+oxytocin, and stress+saline groups. Restraint stress was applied to all the stress groups for 1 h/day, for 7 days. Learning-memory tests were performed after the 7th day.
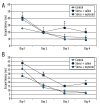
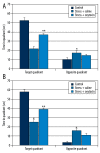
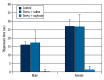
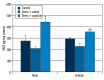
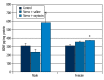
Results: In the stress+oxytocin groups, the process of finding the platform was shorter than in others groups. The stress+saline groups spent less time, whereas the stress+oxytocin groups spent more time, on the target quadrant in the probe trial. In the stress+oxytocin groups thigmotaxis time (indicating anxiety) decreased, but VEGF and BDNF levels increased. A positive correlation was found between VEGF and BDNF levels and the time spent within the target quadrant.
Conclusions: The results indicate that impaired hippocampal learning and memory loss due to chronic restraint stress can be positively affected by intranasal oxytocin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of voluntary and involuntary exercise on cognitive functions, and VEGF and BDNF levels in adolescent rats.Biotech Histochem. 2015 Jan;90(1):55-68. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2014.946968. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Biotech Histochem. 2015. PMID: 25203492
-
Dose dependent effects of oxytocin on cognitive defects and anxiety disorders in adult rats following acute infantile maternal deprivation stress.Biotech Histochem. 2019 Oct;94(7):469-480. doi: 10.1080/10520295.2018.1528384. Epub 2019 May 20. Biotech Histochem. 2019. PMID: 31104534
-
Acute footshock-stress increases spatial learning-memory and correlates to increased hippocampal BDNF and VEGF and cell numbers in adolescent male and female rats.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Apr 18;514(2):141-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.02.049. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 22426107
-
Maternal voluntary exercise ameliorates learning deficit in rat pups exposed, in utero, to valproic acid; role of BDNF and VEGF and their receptors.Neuropeptides. 2018 Oct;71:43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Neuropeptides. 2018. PMID: 30144942
-
ADH and oxytocin in age-related minor cognitive impairment.Aging (Milano). 1997;9(4 Suppl):36-7. doi: 10.1007/BF03339697. Aging (Milano). 1997. PMID: 9358876 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Oxytocin Differentiated Effects According to the Administration Route in a Prenatal Valproic Acid-Induced Rat Model of Autism.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 May 29;56(6):267. doi: 10.3390/medicina56060267. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32485966 Free PMC article.
-
Translational relevance of rodent models of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function and stressors in adolescence.Neurobiol Stress. 2016 Aug 29;6:31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2016.08.003. eCollection 2017 Feb. Neurobiol Stress. 2016. PMID: 28229107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conditional Deletion of Hippocampal CA2/CA3a Oxytocin Receptors Impairs the Persistence of Long-Term Social Recognition Memory in Mice.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 31;38(5):1218-1231. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1896-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 26. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29279308 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between BDNF and oxytocin.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2023 Sep 4;16:100207. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2023.100207. eCollection 2023 Nov. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37868112 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of miR-150 in Stress-Induced Anxiety-Like Behavior in Mice.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jan;35(1):160-172. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9943-x. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30120712
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Vann SD, Oswald CJ, et al. Identifying cortical inputs to the rat hippocampus that subserve allocentric spatial processes: a simple problem with a complex answer. Hippocampus. 2000;10:466–74. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson L, Sapolsky R. The role of the hippocampus in feedback regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Endocr Rev. 1991;12:118–34. - PubMed
-
- Tomar A, Polygalov D, Chattarji S, McHugh TJ. The dynamic impact of repeated stress on the hippocampal spatial map. Hippocampus. 2014 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Sousa N, Lukoyanov NV, Madeira MD, et al. Reorganization of the morphology of hippocampal neurites and synapses after stress-induced damage correlates with behavioral improvement. Neuroscience. 2000;97:253–66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

