Biochemical characterization of RecA variants that contribute to extreme resistance to ionizing radiation
- PMID: 25559557
- PMCID: PMC4308431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.12.001
Biochemical characterization of RecA variants that contribute to extreme resistance to ionizing radiation
Abstract
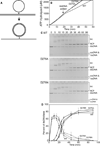
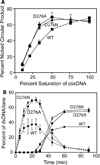
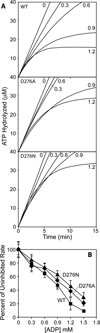
Among strains of Escherichia coli that have evolved to survive extreme exposure to ionizing radiation, mutations in the recA gene are prominent and contribute substantially to the acquired phenotype. Changes at amino acid residue 276, D276A and D276N, occur repeatedly and in separate evolved populations. RecA D276A and RecA D276N exhibit unique adaptations to an environment that can require the repair of hundreds of double strand breaks. These two RecA protein variants (a) exhibit a faster rate of filament nucleation on DNA, as well as a slower extension under at least some conditions, leading potentially to a distribution of the protein among a higher number of shorter filaments, (b) promote DNA strand exchange more efficiently in the context of a shorter filament, and (c) are markedly less inhibited by ADP. These adaptations potentially allow RecA protein to address larger numbers of double strand DNA breaks in an environment where ADP concentrations are higher due to a compromised cellular metabolism.
Keywords: DNA repair; Double strand break repair; Evolution; Radiation resistance; RecA protein.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
RecA protein reinitiates strand exchange on isolated protein-free DNA intermediates. An ADP-resistant process.J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):789-809. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80264-5. J Mol Biol. 1990. PMID: 2141651
-
Biochemical basis of the constitutive coprotease activity of RecA P67W protein.Biochemistry. 2003 May 20;42(19):5937-44. doi: 10.1021/bi027232q. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12741852
-
Biochemical characterization of a mutant RecA protein altered in DNA-binding loop 1.Biochemistry. 2003 May 20;42(19):5945-54. doi: 10.1021/bi027233i. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12741853
-
Relating biochemistry to biology: how the recombinational repair function of RecA protein is manifested in its molecular properties.Bioessays. 1993 Sep;15(9):617-23. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150908. Bioessays. 1993. PMID: 8240315 Review.
-
RecA: Regulation and Mechanism of a Molecular Search Engine.Trends Biochem Sci. 2016 Jun;41(6):491-507. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 May 4. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016. PMID: 27156117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Metabolism in Balance: Rapid Loss of a RecA-Based Hyperrec Phenotype.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 28;11(4):e0154137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154137. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27124470 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental evolution of extremophile resistance to ionizing radiation.Trends Genet. 2021 Sep;37(9):830-845. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.04.011. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Trends Genet. 2021. PMID: 34088512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinational branch migration by the RadA/Sms paralog of RecA in Escherichia coli.Elife. 2016 Feb 4;5:e10807. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10807. Elife. 2016. PMID: 26845522 Free PMC article.
-
Rad51 facilitates filament assembly of meiosis-specific Dmc1 recombinase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 May 26;117(21):11257-11264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1920368117. Epub 2020 May 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32404423 Free PMC article.
-
A variant of the Escherichia coli anaerobic transcription factor FNR exhibiting diminished promoter activation function enhances ionizing radiation resistance.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 23;14(1):e0199482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199482. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30673695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blasius M, Hubscher U, Sommer S. Deinococcus radiodurans: What belongs to the survival kit? Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008;43:221–238. - PubMed
-
- Cox MM, Battista JR. Deinococcus radiodurans - The consummate survivor. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2005;3:882–892. - PubMed
-
- Daly MJ. Death by protein damage in irradiated cells. DNA Repair. 2012;11:12–21. - PubMed
-
- Battista JR. Against all odds - the survival strategies of Deinococcus radiodurans. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997;51:203–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

