Antiinflammatory effect of sevoflurane in open lung surgery with one-lung ventilation
- PMID: 25559834
- PMCID: PMC4295075
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2014.55.628
Antiinflammatory effect of sevoflurane in open lung surgery with one-lung ventilation
Abstract
Aim: To prospectively assess the antiinflammatory effect of volatile anesthetic sevoflurane in patients undergoing open lung surgery with one lung ventilation (OLV).
Methods: This prospective, randomized study included 40 patients undergoing thoracic surgery with OLV (NCT02188407). The patients were randomly allocated into two equal groups that received either propofol or sevoflurane. Four patients were excluded from the study because after surgery they received blood transfusion or non-steroid antiinflammatory drugs. Inflammatory mediators (interleukins 6, 8, and 10, C-reactive protein [CRP], and procalcitonin) were measured perioperatively. The infiltration of the nonoperated lung was assessed on chest x-rays and the oxygenation index was calculated. The major postoperative complications were counted.
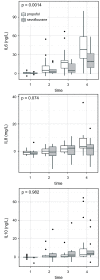
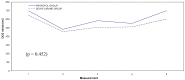
Results: Interleukin 6 levels were significantly higher in propofol than in sevoflurane group (P=0.014). Preoperative CRP levels did not differ between the groups (P=0.351) and in all patients they were lower than 20 mg/L, but postoperative CRP was significantly higher in propofol group (31±6 vs 15±7 ng/L; P=0.035); Pre- and postoperative procalcitonin was within the reference range (<0.04 µg/L) in both groups. The oxygenation index was significantly lower in propofol group (339±139 vs 465±140; P=0.021). There was no significant difference between the groups in lung infiltrates (P=0.5849). The number of postoperative adverse events was higher in propofol group, but the difference was not-significant (5 vs 1; P=0.115).
Conclusion: The study suggests an antiinflammatory effect of sevoflurane in patients undergoing thoracotomy with OLV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Effect of Propofol and Volatile Anesthetics on Postoperative Pulmonary Complications After Lung Resection Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Anesth Analg. 2021 Oct 1;133(4):949-957. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005334. Anesth Analg. 2021. PMID: 33410611 Clinical Trial.
-
Sevoflurane Abolishes Oxygenation Impairment in a Long-Term Rat Model of Acute Lung Injury.Anesth Analg. 2017 Jan;124(1):194-203. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001530. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 27782948
-
Anesthetic-induced improvement of the inflammatory response to one-lung ventilation.Anesthesiology. 2009 Jun;110(6):1316-26. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181a10731. Anesthesiology. 2009. PMID: 19417610 Clinical Trial.
-
Is time to change to halogenated drugs in cardiac surgery, what do we have to do with propofol?Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(34):5497-505. doi: 10.2174/1570161112666140123105536. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24669970 Review.
-
Effects of Sevoflurane and Propofol During Mechanical Ventilation: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Perianesth Nurs. 2025 Apr 8:S1089-9472(24)00562-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jopan.2024.12.001. Online ahead of print. J Perianesth Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40202471 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between controlled lung collapse and early lung injury in dogs.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3027-3033. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6531. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30214521 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalational versus intravenous anesthetics during one lung ventilation in elective thoracic surgeries: A narrative review.Saudi J Anaesth. 2021 Jul-Sep;15(3):312-323. doi: 10.4103/sja.sja_1106_20. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Saudi J Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 34764838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of propofol and inhaled anesthetics on postoperative complications for the patients undergoing one lung ventilation: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 20;17(10):e0266988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266988. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36264981 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of anaesthesia on cancer growth.Radiol Oncol. 2024 Feb 21;58(1):9-14. doi: 10.2478/raon-2024-0012. eCollection 2024 Mar 1. Radiol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38378027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Sevoflurane vs. Propofol for Inflammatory Responses in Patients Undergoing Lung Resection: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Surg. 2021 Jul 2;8:692734. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.692734. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34277696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeldin RA, Normandin D, Landwig D, Peters RM. Postpneumonectomy pulmonary edema. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1984;87:359–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

